 |
 |
- Search
| Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab > Volume 28(1); 2023 > Article |
|
Abstract
Purpose
Methods
Results
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Table 1.
Notes
Funding
This study received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Fig.┬Ā1.
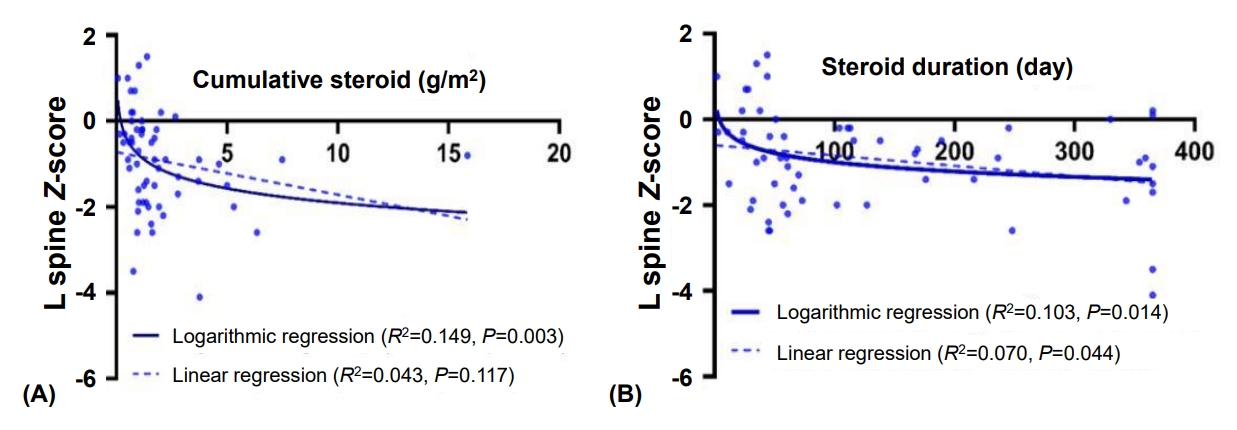
Fig.┬Ā2.
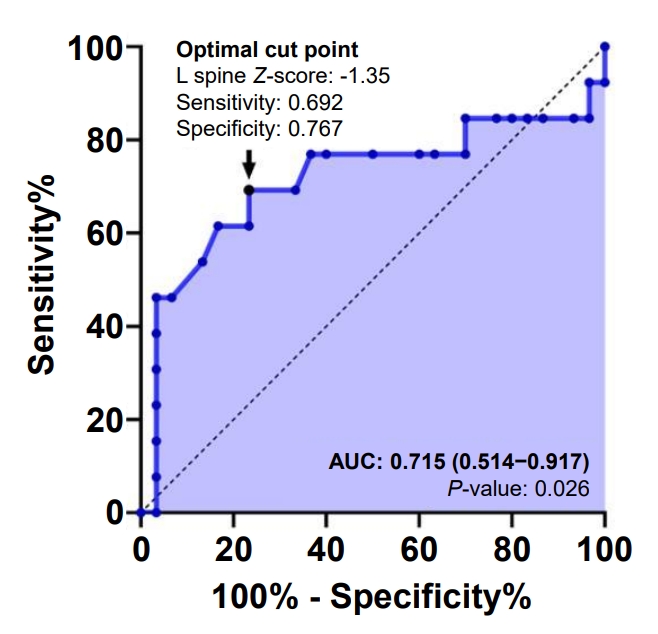
Table┬Ā1.
| Characteristic | Value |
|---|---|
| Male sex | 64 (54.7) |
| Age at diagnosis (yr) | 11 (6ŌĆō13) |
| Classification of underlying disease | |
| ŌĆāHemato-oncology | 92 (78.6) |
| ŌĆāRheumatology | 13 (11.1) |
| ŌĆāGastroenterology | 12 (10.3) |
| Treatment | |
| ŌĆāGlucocorticoidŌĆĀ | 58 (49.6) |
| ŌĆāRadiotherapy | 24 (20.5) |
| ŌĆāStem cell transplantation | 43 (36.8) |
| ŌĆāVitamin D (cholecalciferol or alfacalcidol) | 57 (48.7) |
| Age at initial DXA (yr) | 15 (13ŌĆō16) |
| Z-score at initial DXA | -1.1 (-1.9 to -0.5) |
| ŌĆāŌēż-2.0 | 19 (16.2) |
| ŌĆā>-2.0, Ōēż-1.0 | 30 (25.6) |
| ŌĆā>-1.0 | 68 (58.1) |
| VF at initial DXA | 36 (30.8) |
| Follow-up DXA | 43 (36.8) |
| Age at follow-up DXA (yr) | 16 (14ŌĆō18) |
| Z-score at follow-up DXA | -1.0 (-1.7 to -0.2) |
| ŌĆāŌēż-2.0 | 12 (27.9) |
| ŌĆā>-2.0, Ōēż-1.0 | 11 (25.6) |
| ŌĆā>-1.0 | 20 (46.5) |
| VF at follow-up DXA | 13 (30.2) |
Table┬Ā2.
Values are presented as median (interquartile range), and all biochemical parameters pertain to serum levels.
LSBMD, lumbar spine bone mineral density; SDS, standard deviation score; BMI, body mass index; DXA, dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry; ALP, alkaline phosphatase; PTH, parathyroid hormone; 25(OH)D, 25-hydroxycholecalciferol.
Table┬Ā3.
| Variable |
Unadjusted |
AdjustedŌĆĀ |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | P-value | OR (95% CI) | P-value | ||
| Anthropometry data (SDS) | |||||
| ŌĆāHeight | 1.006 (0.641ŌĆō1.578) | 0.980 | 0.761 (0.371ŌĆō1.560) | 0.456 | |
| ŌĆāWeight | 1.181 (0.800ŌĆō1.742) | 0.403 | 1.499 (0.822ŌĆō2.733) | 0.187 | |
| Glucocorticoid | |||||
| ŌĆāDuration (day)ŌĆĪ | 1.736 (0.963ŌĆō3.128) | 0.067 | 1.741 (0.912ŌĆō3.324) | 0.093 | |
| ŌĆāCumulative dose (mg/m2)ŌĆĪ | 2.226 (1.043ŌĆō4.749) | 0.039 | 2.255 (1.050ŌĆō4.846) | 0.037 | |
| Cholecalciferol intervention | 1.286 (0.404-4.094) | 0.671 | 1.670 (0.479ŌĆō5.825) | 0.421 | |
| Bone metabolic markers | |||||
| ŌĆāCalcium (mg/dL) | 1.111 (0.305ŌĆō4.048) | 0.874 | - | - | |
| ŌĆāPhosphorus (mg/dL) | 1.155 (0.488ŌĆō2.729) | 0.743 | - | - | |
| ŌĆāALP (U/L) | 1.005 (0.998ŌĆō1.011) | 0.153 | - | - | |
| ŌĆāPTH (pg/mL) | 1.000 (0.982ŌĆō1.019) | 0.975 | - | - | |
| ŌĆā25(OH)D | 1.026 (0.956ŌĆō1.100) | 0.476 | - | - | |
DXA, dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry; OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; SDS, standard deviation score; ALP, alkaline phosphatase; PTH, parathyroid hormone; 25(OH)D, 25-hydroxycholecalciferol.
Table┬Ā4.
| Variable |
Unadjusted |
AdjustedŌĆĀ |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | P-value | OR (95% CI) | P-value | ||
| Glucocorticoid | |||||
| ŌĆāCumulative dose (mg/m2)ŌĆĪ | 1.315 (0.399ŌĆō4.337) | 0.653 | 1.301 (0.269ŌĆō6.295) | 0.743 | |
| ŌĆāDuration (day)ŌĆĪ | 1.485 (0.505ŌĆō4.365) | 0.472 | 1.964 (0.495ŌĆō7.794) | 0.337 | |
| ŌĆāCholecalciferol intervention | 0.583 (0.154ŌĆō2.203) | 0.427 | 0.507 (0.122ŌĆō2.106) | 0.350 | |
| Initial LSBMD (SDS) | |||||
| ŌĆāTotal | 0.639 (0.337ŌĆō1.214) | 0.171 | 0.449(0.170ŌĆō1.189) | 0.107 | |
| ŌĆā<-2.0 | 12.000 (1.980ŌĆō72.736) | 0.007 | 31.120 (2.700ŌĆō358.645) | 0.006 | |
| ŌĆā<-1.0 | 3.333 (0.762ŌĆō14.576) | 0.110 | 8.793 (0.712ŌĆō108.529) | 0.090 | |
| ŌĆāŌēż-1.35 | 7.393(1.734ŌĆō31.522) | 0.007 | 11.939 (2.131ŌĆō66.873) | 0.005 | |
| Bone metabolic markers | |||||
| ŌĆāCalcium (mg/dL) | 1.294 (0.184ŌĆō9.093) | 0.796 | - | - | |
| ŌĆāPhosphorus (mg/dL) | 1.234 (0.306ŌĆō4.981) | 0.768 | - | - | |
| ŌĆāALP (U/L) | 0.998 (0.989ŌĆō1.007) | 0.622 | - | - | |
| ŌĆāPTH (pg/mL) | 1.001 (0.980ŌĆō1.023) | 0.938 | - | - | |
| ŌĆā25(OH)D | 1.010 (0.911ŌĆō1.120) | 0.848 | - | - | |
DXA, dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry; OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; LSBMD, lumbar spine bone mineral density; SDS, standard deviation score; ALP, alkaline phosphatase; PTH, parathyroid hormone; 25(OH)D, 25-hydroxycholecalciferol.
References
- TOOLS
- Related articles in APEM
-
Low bone mineral density in children and adolescents with cancer2020 September;25(3)







