 |
 |
- Search
| Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab > Volume 25(3); 2020 > Article |
|
Abstract
Type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) requires life-long insulin therapy because of diminished insulin-secretion capability. Glycemic control and glucose monitoring are important to prevent T1DM complications. Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) measures glucose level, every one to five minutes, in the interstitial fluid from a subcutaneous sensor and facilitates better glycemic control, reduces hypoglycemia, and is safely used in the pediatric population. CGM can be categorized as retrospective, real-time, or intermittently scanned CGM, and all forms are available in Korea. The CGM device has 3 components: sensor, transmitter, and monitor/receiver. Key metrics of CGM include days of CGM application, percentage of time with CGM, mean glucose, glucose management indicator, glycemic variability, and use of Ambulatory Glucose Profile for CGM reports. CGM sensors and transmitters have been partly reimbursed by the Korean National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) since 2019, and 1,434 T1DM patients (male, 40.8%; age <20 years, 52.4%) in Korea were prescribed CGM as of December 2019. In Korea, the number of CGM users will increase due to reimbursement for CGM sensors and transmitters by the NHIS. Successful CGM use requires long-term policies to establish diabetes education and financial assistance. Clinicians should become well-acquainted with interpretation of CGM data and information updates to facilitate integration of CGM data into clinical practice among pediatric T1DM patients.
Type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) is caused by progressive loss of pancreatic beta cells as a consequence of autoimmune destruction that eventually leads to decreased insulin secretion [1,2]. Therefore, life-long insulin therapy is required in patients with T1DM to achieve optimal glycemic control and prevent acute and chronic complications [3]. Recent reports have shown an increasing incidence of T1DM worldwide as well as in Korea, and this might increase the associated burden of disease [4,5].
Self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) and measurement of glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) has been part of the standard care for diabetes management and is considered essential for glycemic control. Frequent measurement (6–10 times per day) of SMBG is associated with decreased HbA1c value [6-8]. SMBG shows blood glucose level at the time of testing but has several disadvantages such as need for a finger-prick and no information on trends between SMBG measurements. HbA1c reflects the average blood glucose level over approximately 3 months. Most of the recent guidelines recommend HbA1c <7.0% in children and adolescents with T1DM [8,9]. HbA1c has advantages such as non-fasting-sample-based measurement, being a reference marker for metabolic control, and strong association with diabetes-related complications [10,11]. However, limitations of HbA1c include its inability to reflect daily glycemic variability and the influence of hemoglobin concentration [12,13].
Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) is a device-based testing method that circumvents the limitations of SMBG and HbA1c. CGM measures glucose level in the interstitial fluid every 1 to 5 minutes from a sensor inserted into subcutaneous tissue [14]. Technological advances in CGM devices have facilitated smaller size, affordable price, and increased accuracy. Several studies have shown CGM improves glycemic control and decreases hypoglycemia. Recent guidelines recommend CGM as an essential consideration for management of T1DM in children and adolescents [15-17]. In Korea, CGM sensors and transmitters have been partly reimbursed by the Korean National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) since 2019 and 2020, respectively. This review summarizes the current status of CGM among Korean children and adolescents with T1DM.
There are 3 main types of CGM systems: retrospective (professional) CGM, real-time (personal) CGM, and intermittently scanned CGM (isCGM, or flash glucose monitoring). Retrospective CGM measures glucose continuously, blinded to patient. After 10 to 14 days of CGM, the data are analyzed in a clinic by healthcare providers. Real-time CGM measures glucose value continuously; unblinded to patient; and provides real-time glucose level, alarms for preset threshold, hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, as well as glucose trends and predictions. Recently developed CGM systems have the capacity to transmit data to cloud storage, which enables sharing and tracing of CGM data among caregivers and healthcare providers. The isCGM measures glucose continuously but only shows glucose level at the time of sensor scan. In Korea, as of September 2020, 3 real-time CGM and 1 isCGM systems are available: the GuardianTM Connect CGM system (Medtronic Inc., Minneapolis, MN, USA), the Dexcom G5Ⓡ Mobile CGM system (Dexcom Inc, San Diego, CA, USA), and the FreeStyleⓇ Libre (Abbott Diabetes Care Limited, Witney, Oxfordshire, UK).
The CGM system has 3 components: sensor, transmitter, and monitor (receiver). The sensors are inserted into subcutaneous tissue and measure glucose level in the interstitial fluid for 6 to 14 days, depending on manufacturer. Most CGM sensors need to be calibrated at least twice daily, although isCGM sensors do not need recalibration as they are factory calibrated. Furthermore, "adjunctive" CGM devices require SMBG confirmation for therapeutic decision making, whereas "nonadjunctive" devices do not. Transmitters send the glucose measurement data to a monitor or receiver and may be functional for 3 months or 1 year based on the manufacturer. However, the isCGM does not have a transmitter and, instead, utilizes a monitor/receiver to receive and display data from a transmitter, such as a smartphone, smartwatch, or company-manufactured display terminal.
The key metrics for CGM data analysis were suggested in the Advanced Technologies & Treatments for Diabetes (ATTD) consensus recommendations of 2017 [15]. The recent ATTD consensus recommendations of 2019 suggested the use of standardized CGM metrics for clinical care [18]. Ten core metrics and recommendations for T1DM patients were selected: (1) number of days of CGM application (14 days) [19], (2) percentage of time with CGM (at least 70% of data from 14 days), (3) mean glucose, (4) glucose management indicator (formerly, estimated HbA1c) [20], (5) glycemic variability as % of coefficient of variation (≤36%), (6) time above range as % of readings and time >250 mg/dL (<5%), (7) time above range as % of readings and time 181–250 mg/dL (<25%), (8) time in range as % of readings and time 70–180 mg/dL (>70%), (9) time below range as % of readings and time 54–69 mg/dL (<4%), (10) time below range as % of readings and time <54 mg/dL (<1%), and use of Ambulatory Glucose Profile (AGP) for CGM reports.
The AGP report is a standardized, single-page report of CGM [21]. The updated version 4.0 of the AGP report displays 10 key metrics for CGM in "Glucose Statistics and Targets" and "Time in Range" sections (Fig. 1). Moreover, a graph presents the median along with 5th, 25th, 75th, and 95th percentile lines and target range (70–180 mg/dL) of the glucose profile over a 24-hour period, which summarizes glucose values from the reported period. In addition, daily glucose profiles are displayed.
In Korea, the software packages available for CGM data analysis are CareLinkTM for GuardianTM Connect CGM system, Dexcom CLARITYⓇ for Dexcom G5Ⓡ Mobile CGM system and Dexcom G6Ⓡ CGM system, and LibreViewⓇ for FreeStyleⓇ Libre. Using these software packages, key metrics of CGM can be analyzed and reported (Fig. 2).
Several studies have reported that glycemic control is improved in pediatric T1DM patients who use CGM. In a study from the Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation on CGM use, HbA1c decreased by 0.5% in adults but showed no significant difference in participants younger than 25 years due to poor adherence to CGM [22]. However, secondary analysis in a younger age group showed improved glycemic control with ≥6 days/wk of adherence [23]. Moreover, CGM was beneficial in maintaining good glycemic control and decreasing hypoglycemia in individuals with HbA1c <7.0% [24]. Further, CGM was effective in reducing HbA1c and glycemic variability, especially in participants who availed nearly daily application [25,26]. In a study among T1DM patients younger than 4 years, caregivers showed high satisfaction for CGM use with regard to hypoglycemia and effect on habits influencing glycemia and insulin-dose adjustment, although glycemic control was unsatisfactory [27].
In adult patients with T1DM, the use of CGM is associated with decreased episodes of hypoglycemia, especially in high-risk populations with hypoglycemia unawareness and/or severe hypoglycemic event [28-30]. In pediatric T1DM patients, several studies have shown decreased time spent in hypoglycemia and hypoglycemic episodes [24,31], although some studies did not report this benefit [22,32]. CGM might be helpful for high-risk pediatric patients with T1DM similarly as in adults. Further studies with updated CGM systems are needed in children and adolescents with T1DM.
In Korea, 3 types of real-time CGM, retrospective CGM and isCGM, are approved by the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety of Korea. The characteristics of CGM systems are summarized in Table 1.
Sensors and transmitters (and insulin pumps) of CGM systems have been reimbursed partially by the NHIS since January 2019 and January 2020, respectively. Approximately 40%–50% of the total cost of sensors and transmitters for CGM are paid by patients or caregivers. Following approval by the regulatory agencies in 2018, isCGM will become commercially available from May 2020. However, retrospective CGM is not covered by the NHIS of Korea.
According to the claim data of the NHIS, as of December 2019 a total of 19,730 patients with T1DM (4,021 aged <20 years and 15,709 aged ≥20 years) were registered in the NHIS for reimbursement of diabetes management expendables. Among them, 1,434 patients (7.3%) with T1DM were prescribed CGM sensors from January to December 2019. Of these individuals, 585 (40.8%) were male and 849 (59.2%) were female, while 751 (52.4%) were younger than 20 years and 683 (47.6%) were 20 years of age or older (Table 2). No sex differences were identified by age group (P=0.147). In the United States, 4% and 19% of CGM users in 2011 and 2016, respectively, were T1DM patients younger than 18 years registered in the T1DM Exchange Clinic Registry. In the Prospective Diabetes Follow-Up Registry (DPV) from Germany and Austria, 3% and 22% of the participants aged <18 years were CGM users in 2011 and 2016, respectively [33,34]. The proportion of CGM users among Korean T1DM patients younger than 20 years of age was 18.7% in 2019, which is similar to the data recorded by the T1DM Exchange Clinic Registry but slightly lower than that in the DPV registry. However, the number of actual CGM users in Korea may be underestimated because some isCGM and real-time CGM users may not have claimed reimbursement for sensors. Further, CGM users with type 2 diabetes or gestational diabetes were not included in the claim data. Nonetheless, CGM users in Korea are expected to increase continually given the introduction of partial reimbursements for CGM transmitters and insulin pumps since January 2020.
Successful CGM application requires education, training, and frequent contact with healthcare providers, as well as education for diabetes self-management [35,36]. Therefore, healthcare structures which provide fee-for-service educational programs delivered by experienced diabetes educators need to be improved for successful initiation and use of CGM for individuals.
CGM is an effective technology for facilitating better glycemic control and reducing hypoglycemia and can be used safely in the pediatric population. With recent advances in systems, CGM has become an essential consideration in management of pediatric T1DM patients. Korean CGM users are expected to increase with reimbursement of CGM sensors and transmitters by the NHIS. For successful CGM use, there is a need for implementation of a long-term policy for diabetes education and financial assistance related to CGM. Technologies for managing diabetes, including CGM, are rapidly being updated, and clinicians should acquaint themselves with interpretation of CGM data and informational updates given the importance of integrating CGM data into clinical practice among pediatric T1DM patients.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The author thanks Yoo Kyung Yoon and Sun Hye Moon of the Department of Benefits Assurance of the National Health Insurance Service, Korea, for research collaboration and access to data.
Fig. 1.
Ambulatory glucose profile report (v4.0) for continuous glucose monitoring by the International Diabetes Center (Available at: http://www.agpreport.org/agp/sites/default/files/2_About_CGM_AGP_V4.PNG). Adapted from International Diabetes Center for publication with permission.

Fig. 2.
Screenshot from the continuous glucose monitoring software. (A) Dexcom CLARITYⓇ for Dexcom G5Ⓡ Mobile CGM system. (B) CareLinkTM for GuardianTM Connect CGM system.
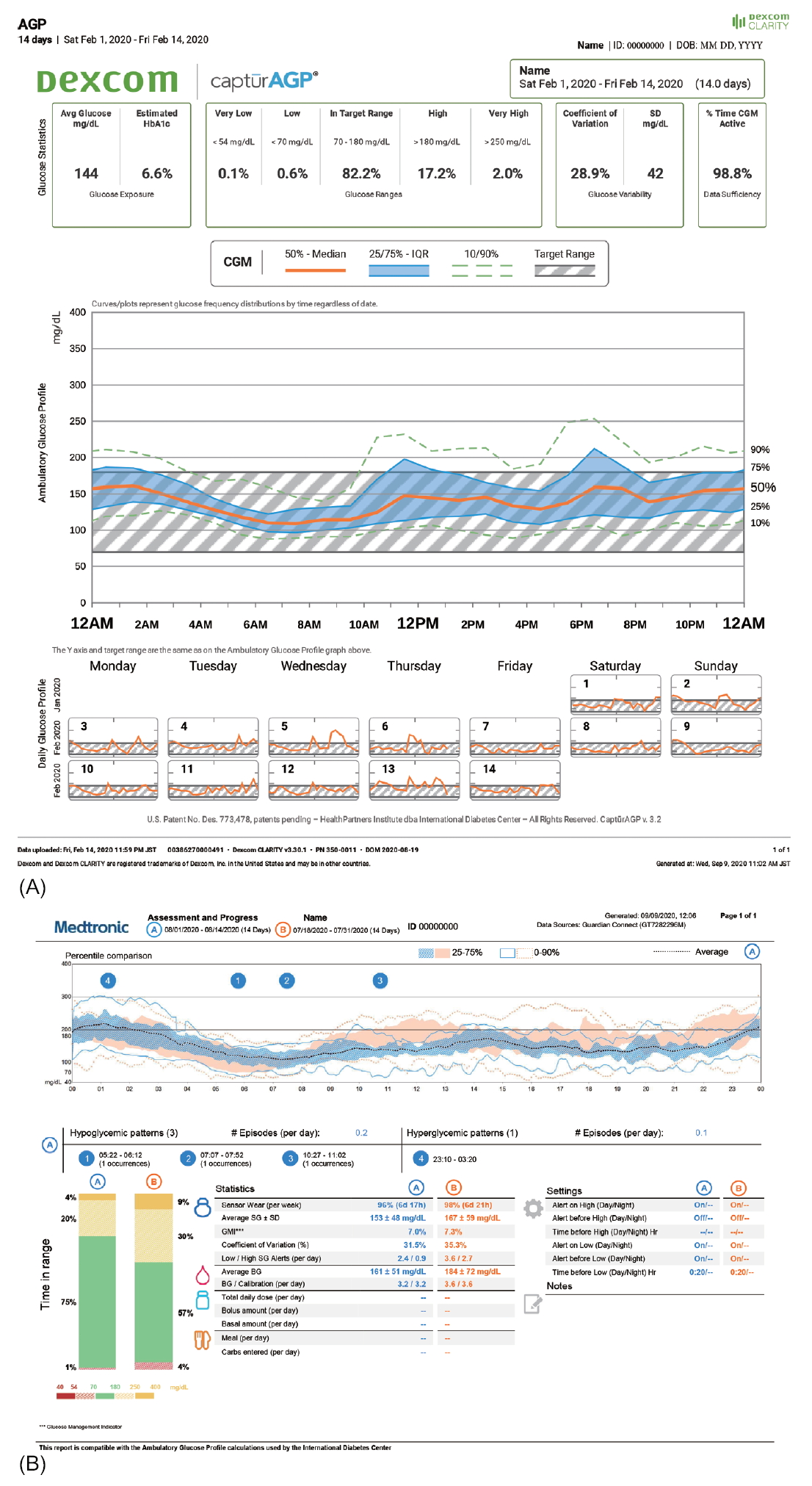
Table 1.
Characteristics of available continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems in Korea
| Model | GuardianTM Connect CGM system | Dexcom G5® Mobile CGM system | Dexcom G6® CGM system | FreeStyle® Libre | iPro2 Professional CGM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Medtronic | Dexcom Inc. | Dexcom Inc. | Abbott Diabetes Care | Medtronic |
| Type | Real time | Real time | Real time | Intermittently scanned | Retrospective |
| Age | All ages | ≥2 Years | ≥2 Years | ≥4 Years | All ages |
| Sensor duration | 6 Days (Enlite sensor) | 7 Days | 10 Days | 14 Days | 6 Days |
| 7 Days (Guardian 3 sensor) | |||||
| Calibration | Every 12 hours | Every 12 hours | No (factory-calibrated) | No (factory-calibrated) | Every 6 hours |
| MARD | Enlite sensor: 13.6% | 9%–10% | Overall 9% | 11.40% | 11.0%–12.2% |
| Guardian 3 sensor: 8.7%–10.5% | |||||
| Warranty of transmitter | 1 Year | 3 Months | 3 Months | - | - |
| Acetaminophen interference | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| Reimbursement | Yes | Yes | No* | No* | No |
| Software | CareLinkTM | Dexcom CLARITY® | Dexcom CLARITY® | LibreView® | CareLinkTM iPro |
Table 2.
Number of patients with T1DM in Korea who were prescribed sensors for continuous glucose monitoring between January and December 2019
References
2. Ilonen J, Lempainen J, Veijola R. The heterogeneous pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2019;15:635–50.



3. Nathan DM, DCCT/EDIC Research Group. The diabetes control and complications trial/epidemiology of diabetes interventions and complications study at 30 years: overview. Diabetes Care 2014;37:9–16.


4. Kim JH, Lee CG, Lee YA, Yang SW, Shin CH. Increasing incidence of type 1 diabetes among Korean children and adolescents: analysis of data from a nationwide registry in Korea. Pediatr Diabetes 2016;17:519–24.


5. Patterson C, Guariguata L, Dahlquist G, Soltész G, Ogle G, Silink M. Diabetes in the young - a global view and worldwide estimates of numbers of children with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2014;103:161–75.


6. Ziegler R, Heidtmann B, Hilgard D, Hofer S, Rosenbauer J, Holl R, et al. Frequency of SMBG correlates with HbA1c and acute complications in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Pediatr Diabetes 2011;12:11–7.


7. Chiang JL, Kirkman MS, Laffel LM, Peters AL, Type 1 Diabetes Sourcebook Authors. Type 1 diabetes through the life span: a position statement of the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2014;37:2034–54.



8. DiMeglio LA, Acerini CL, Codner E, Craig ME, Hofer SE, Pillay K, et al. ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines 2018: glycemic control targets and glucose monitoring for children, adolescents, and young adults with diabetes. Pediatr Diabetes 2018;19 Suppl 27:105–14.


9. American Diabetes Association. 13. Children and adolescents: standards of medical care in diabetes-2020. Diabetes Care 2020;43:S163–82.



10. Writing Group for the DCCT/EDIC Research Group; Orchard TJ, Nathan DM, Zinman B, Cleary P, Brillon D, et al. Association between 7 years of intensive treatment of type 1 diabetes and long-term mortality. JAMA 2015;313:45–53.



11. Holman RR, Paul SK, Bethel MA, Matthews DR, Neil HA. 10-year follow-up of intensive glucose control in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2008;359:1577–89.


12. Bry L, Chen PC, Sacks DB. Effects of hemoglobin variants and chemically modified derivatives on assays for glycohemoglobin. Clin Chem 2001;47:153–63.



13. Ford ES, Cowie CC, Li C, Handelsman Y, Bloomgarden ZT. Iron-deficiency anemia, non-iron-deficiency anemia and HbA1c among adults in the US. J Diabetes 2011;3:67–73.


14. Cappon G, Vettoretti M, Sparacino G, Facchinetti A. Continuous glucose monitoring sensors for diabetes management: a review of technologies and applications. Diabetes Metab J 2019;43:383–97.



15. Danne T, Nimri R, Battelino T, Bergenstal RM, Close KL, DeVries JH, et al. International consensus on use of continuous glucose monitoring. Diabetes Care 2017;40:1631–40.



16. Sherr JL, Tauschmann M, Battelino T, de Bock M, Forlenza G, Roman R, et al. ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines 2018: diabetes technologies. Pediatr Diabetes 2018;19 Suppl 27:302–25.


17. American Diabetes Association. 7. Diabetes technology: standards of medical care in diabetes-2020. Diabetes Care 2020;43:S77–88.



18. Battelino T, Danne T, Bergenstal RM, Amiel SA, Beck R, Biester T, et al. Clinical targets for continuous glucose monitoring data interpretation: recommendations from the International Consensus on Time in Range. Diabetes Care 2019;42:1593–603.



19. Riddlesworth TD, B eck RW, Gal RL, C onnor CG, Bergenstal RM, Lee S, et al. Optimal sampling duration for continuous glucose monitoring to determine long-term glycemic control. Diabetes Technol Ther 2018;20:314–6.


20. Bergenstal RM, Beck RW, Close KL, Grunberger G, Sacks DB, Kowalski A, et al. Glucose Management Indicator (GMI): a new term for estimating A1C from continuous glucose monitoring. Diabetes Care 2018;41:2275–80.



21. International Diabetes Center. AGP - Ambulatory Glucose Profile [Internet] International Diabetes Center. 2020;[2020 Mar 5]. Available from: http://www.agpreport.org/agp/.
22. Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation Continuous Glucose Monitoring Study Group; Tamborlane WV, Beck RW, Bode BW, Buckingham B, Chase HP, et al. Continuous glucose monitoring and intensive treatment of type 1 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2008;359:1464–76.


23. Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation Continuous Glucose Monitoring Study Group; Beck RW, Buckingham B, Miller K, Wolpert H, Xing D, et al. Factors predictive of use and of benefit from continuous glucose monitoring in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2009;32:1947–53.



24. Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation Continuous Glucose Monitoring Study Group; Beck RW, Hirsch IB, Laffel L, Tamborlane WV, Bode BW, et al. The effect of continuous glucose monitoring in well-controlled type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2009;32:1378–83.



25. Pickup JC, Freeman SC, Sutton AJ. Glycaemic control in type 1 diabetes during real time continuous glucose monitoring compared with self monitoring of blood glucose: meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials using individual patient data. Version 2. BMJ 2011;343:d3805.



26. Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation Continuous Glucose Monitoring Study Group. Effectiveness of continuous glucose monitoring in a clinical care environment: evidence from the Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation continuous glucose monitoring (JDRF-CGM) trial. Diabetes Care 2010;33:17–22.

27. Tsalikian E, Fox L, Weinzimer S, Buckingham B, White NH, Beck R, et al. Feasibility of prolonged continuous glucose monitoring in toddlers with type 1 diabetes. Pediatr Diabetes 2012;13:301–7.


28. Hermanns N, Schumann B, Kulzer B, Haak T. The impact of continuous glucose monitoring on low interstitial glucose values and low blood glucose values assessed by point-of-care blood glucose meters: results of a crossover trial. J Diabetes Sci Technol 2014;8:516–22.



29. Bolinder J, Antuna R, Geelhoed-Duijvestijn P, Kröger J, Weitgasser R. Novel glucose-sensing technology and hypoglycaemia in type 1 diabetes: a multicentre, non-masked, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2016;388:2254–63.


30. van B eers CA, DeVries JH, Kleijer SJ, Smits MM, Geelhoed-Duijvestijn PH, Kramer MH, et al. Continuous glucose monitoring for patients with type 1 diabetes and impaired awareness of hypoglycaemia (IN CONTROL): a randomised, open-label, crossover trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2016;4:893–902.


31. Battelino T, Phillip M, Bratina N, Nimri R, Oskarsson P, Bolinder J. Effect of continuous glucose monitoring on hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2011;34:795–800.



32. Mauras N, Beck R, Xing D, Ruedy K, Buckingham B, Tansey M, et al. A randomized clinical trial to assess the efficacy and safety of real-time continuous glucose monitoring in the management of type 1 diabetes in young children aged 4 to <10 years. Diabetes Care 2012;35:204–10.



33. Foste r NC, Beck RW, Miller KM, Clements MA, Rickels MR, DiMeglio LA, et al. State of type 1 diabetes management and outcomes from the T1D exchange in 2016-2018. Diabetes Technol Ther 2019;21:66–72.



34. DeSalvo DJ, Miller KM, Hermann JM, Maahs DM, Hofer SE, Clements MA, et al. Continuous glucose monitoring and glycemic control among youth with type 1 diabetes: International comparison from the T1D Exchange and DPV Initiative. Version 2. Pediatr Diabetes 2018;19:1271–5.










