 |
 |
- Search
| Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab > Volume 23(4); 2018 > Article |
|
Abstract
Most cases of congenital hyperthyroidism are autoimmune forms caused by maternal thyroid stimulating antibodies. Nonautoimmune forms of congenital hyperthyroidism caused by activating mutations of the thyrotropin receptor (TSHR) gene are rare. A woman gave birth to a boy during an emergency cesarean section at 33 weeks of gestation due to fetal tachycardia. On the 24th day of life, thyroid function tests were performed due to persistent tachycardia, and hyperthyroidism was confirmed. Auto-antibodies to TSHR, thyroid peroxidase, and thyroglobulin were not found. The patient was treated with propylthiouracil and propranolol, but hyperthyroidism was not well controlled. At 3 months of age, the patient had craniosynostosis and hydrocephalus, and underwent a ventriculoperitoneal shunt operation. Direct sequencing of the TSHR gene showed a heterozygous mutation of c.1899C>A (p.Asp633Glu) in exon 10. No mutations were discovered in any of the parents in a familial genetic study. We have reported a case of sporadic nonautoimmune congenital hyperthyroidism, by a missense mutation of the TSHR gene, for the first time in South Korea.
Congenital hyperthyroidism caused by activating mutations of the thyrotropin receptor (TSHR) gene is a rare disorder. Most cases of congenital hyperthyroidism are autoimmune forms caused by maternal thyroid stimulating immunoglobulins. Autoimmune congenital hyperthyroidism shows a transient course, lasting approximately 4 months after birth, and resolving when maternal antibodies are eliminated from the blood of the infant. However, nonautoimmune congenital hyperthyroidism by activating germline mutations in the TSHR gene shows a persistent and severe hyperthyroidism. Clinical manifestations of nonautoimmune congenital hyperthyroidism might occur from the fetus and cause tachycardia, arrhythmia, intrauterine growth retardation and premature birth. There are 2 types of activating TSHR germline mutations. One is familial nonautoimmune hyperthyroidism (FNAH), an autosomal dominant disorder, and the other is sporadic nonautoimmune hyperthyroidism (SNAH), caused by de novo mutations [1]. Compared to FNAH, SNAH tends to occur at a younger age, present more severe clinical symptoms. These findings might be influenced by genetic, epigenetic or environmental factors including in vitro activity of TSHR mutations [2]. To date, a total of 17 patients with SNAH by 12 activating mutations of the TSHR gene have been reported in the literature [2-4]. Herein, we report a case of sporadic nonautoimmune congenital hyperthyroidism by a missense mutation of the TSHR gene for the first time in South Korea.
A woman gave birth to a boy during an emergency cesarean section at 33 weeks of gestation due to fetal tachycardia. The birth weight was 2,280 g (50thŌĆō75th percentile), height was 43 cm (10thŌĆō25th percentile), and head circumference was 31 cm (50thŌĆō75th percentile). After birth, the boy was treated with meconium aspiration syndrome in neonatal intensive care unit. Approximately 4 days later, the patient recovered with mechanical ventilation, but continued to have tachycardia. Electrocardiography and echocardiography was normal except sinus tachycardia. Thyroid function test showed hyperthyroidism with increased free thyroxine (fT4, 3.98 ng/dL; normal reference value, 0.85ŌĆō1.86 ng/dL), total triiodothyronine (T3, 10.52 ng/mL; normal reference value, 0.78ŌĆō1.82 ng/mL) and decreased thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH, 0.05 mIU/L; normal reference value, 0.17ŌĆō4.05 mIU/L). Test for antibodies to TSHR, thyroid peroxidase, and thyroglobulin were negative. A thyroid ultrasound revealed increased vascularity and a diffuse goiter. The patient's mother had no history of any thyroid disease.
The patient was treated with propylthiouracil (PTU, 5 mg/kg) and propranolol for short-term management of thyroid storm [5], but showed persistent hyperthyroidism even after 1 month of treatment. One more month of intensive treatment with an increased dose of PTU (7.5 mg/kg) could only lead to subclinical hyperthyroidism (fT4, 1.07 ng/dL; T3, 2.54 ng/mL; TSH, 0.01 mIU/L). At 3 months after birth, a forehead protrusion was observed and the anterior fontanelle could not be palpated on physical examination. Brain computed tomography revealed hydrocephalus due to craniosynostosis and the patient underwent surgery to place a ventriculoperitoneal shunt. After 6 more months of treatment, thyroid function tests recovered to normal and tachycardia improved. PTU treatment was replaced with methimazole and euthyroid state was maintained for 2 months. When the dose of methimazole was reduced (0.3 mg/kg), a relapse of hyperthyroidism occurred. At 12 months of age (corrected age of 10 months), the patientŌĆÖs height and weight were in the 50thŌĆō75th and 25thŌĆō50th percentile, respectively, in addition to exhibiting delayed milestones (cognitive skills at 7 months, receptive communication at 5 months, expressive communication at 6 months, fine motor at 6 months, and gross motor at 7 months). Moreover, the patientŌĆÖs bone age was estimated to be 2 years and 8 months, which was markedly advanced compared to his chronological age.
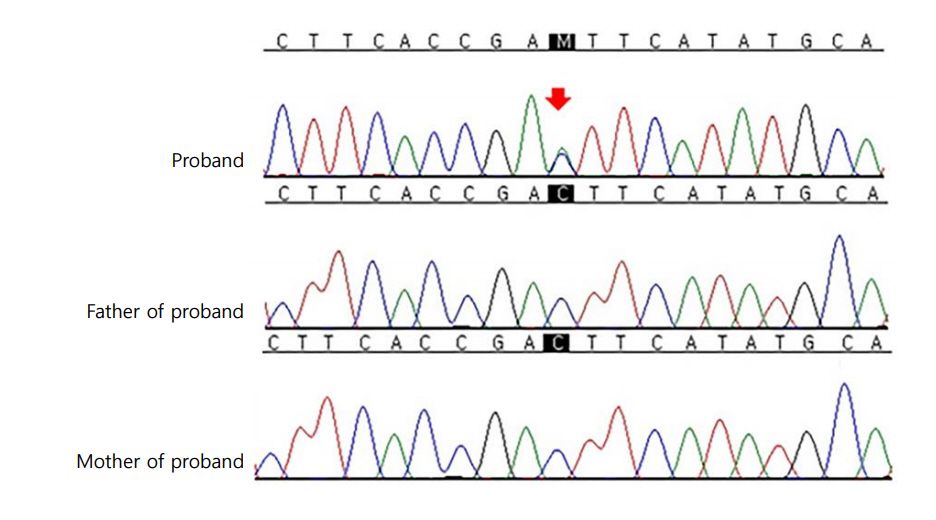
Molecular genetic analysis was performed by direct sequencing of TSHR. Genomic DNA was isolated from peripheral blood leukocytes using a QIAmp DNA Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was performed using gene-specific primers for all coding exons and splice junctions of TSHR as previously described [6]. PCR amplicons were bi-directionally sequenced using the BigDye Terminator v3.1 Cycle Sequencing Kit (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) on an ABI PRISM 3100 Genetic Analyzer (Applied Biosystems). DNA chromatograms were analyzed using Sequencher software version 5.0 (Gene Codes, Ann Arbor, MI, USA) and the mutation was described according to the Human Genome Variation Society nomenclature. RefSeq ID: NM_000369.2 was used for reference sequences. Direct sequencing of the PCR products revealed the heterozygous missense mutation of c.1899C>A (p.Asp633Glu) in exon 10 of TSHR. No mutation was observed in all parents in a familial genetic study (Fig. 1). Therefore, c.1899C>A (p.Asp633Glu) was deemed a de novo mutation. The variant was neither found in ExAC nor 1000 genomes. In In silico analysis, the variant was predicted deleterious by SIFT (http://provean.jcvi.org/protein_batch_submit.php), probably damaging by Polyphen-2 (http://genetics.bwh.harvard.edu/pph2/) and disease causing by Mutation Taster (http://www.mutationtaster.org/). The patient continues to be treated with antithyroid medication and maintains a euthyroid state.
This report was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) at the Catholic University of Korea, Seoul St. MaryŌĆÖs Hospital. Informed consent was waived by the IRB.
In 1995, SNAH was first reported by Kopp et al. [1], who characterized it as severe thyrotoxicosis during the neonatal period or infancy. Table 1 summarizes the clinical features of 17 patients with sporadic non-autoimmune congenital hyperthyroidism by 12 activating mutations of the TSHR gene. Most of the SNAH patients who have been reported to date have exhibited manifestations of hyperthyroidism during the newborn period [1,4,6-15]. Many of the reported SNAH patients were born prematurely or with a low birth weight [1,6,8-13]. In particular, the patient reported by Holzapfel et al. [16] presented with thyrotoxicosis during the fetal period. The patient in the present study was born prematurely as well and presented with tachycardia during the fetal period. In addition, the patient had thyroid hypertrophy, craniosynostosis with advanced bone age, poor weight gain, and mild developmental delay. These clinical features are similar to other SNAH patients. Specifically, craniosynostosis was reported in 7 patients, while advanced bone age was confirmed in 12 patients. Moreover, there have been five SNAH patients without goiter and proptosis was documented in 7 of the 17 patients. Additional symptoms that have been reported for SNAH patients include jaundice, diarrhea, apnea, asphyxia, and hepatosplenomegaly. To date, a total of 12 TSHR gene mutations in less than 20 cases have been reported; however, there is no definite genotype-phenotype relationship (Table 1).
Somatic mutations of TSHR residue 633 (p.Asp633Glu, p.Asp633Tyr, p.Asp633His, and p.Asp633Ala) have been reported for an autonomously functioning thyroid nodule as well as toxic thyroid adenoma tissue of patients with hyperthyroidism. The same amino acid residue was also reported to be altered in a previous case of nonautoimmune congenital hyperthyroidism, consisting of an aspartate to tyrosine substitution [9]. However, because of the different base substitution, the patient in this report has a novel missense variant. In addition, this is the first report of SNAH in South Korea. For treatment of nonautoimmune congenital hyperthyroidism, antithyroid drugs, such as PTU or methimazole, are used. However, several reported cases were not adequately treated with medication alone, eventually requiring ablative treatment such as radioiodine therapy or thyroidectomy [1,9,10,12,14]. At present, the patient in this report is being treated with antithyroid medication alone. If diagnosis and treatment are delayed, nonautoimmune congenital hyperthyroidism may cause irreversible complications such as mental retardation. Therefore, early diagnosis and prompt treatment with genetic counseling are necessary.
In conclusion, we identified a new case of SNAH caused by an activating mutation of the TSHR gene in a premature newborn with persistent tachycardia after birth. To date, a total of 12 activating mutations of the TSHR gene in less than 20 cases have been reported. Unlike autoimmune congenital hyperthyroidism, SNAH shows a persistent and severe hyperthyroidism. Furthermore, thyroidectomy and radioactive iodine therapy are inevitable to prevent long-term complications. The diagnosis is challenging due to lack of genotype-phenotype correlation, thus early genetic screening is a key to minimizing permanent sequelae.
Fig.┬Ā1.
Direct sequencing analysis of TSHR. The proband was heterozygous for the missense mutation c.1899C>A (p.Asp633Glu). The same base change was not present in his father or mother. The base substitution mutation is indicated by a red arrow.
Table┬Ā1.
Clinical features of 17 patients with sporadic nonautoimmune congenital hyperthyroidism by 12 activating mutation of the TSHR gene
| Case | Onset of hyperthyroidism | Gestational age/birth weight | Clinical manifestation related to hyperthyroidism | Mutation | Treatment | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fetal period | 38 wk/2,410 g | Fetal tachycardia, advanced bone age, poor weight gain | p.Ser281Asn | Antithyroid drugs | Scaglia et al. [17] |
| Total thyroidectomy | ||||||
| 2 | Fetal period | 38 wk/2,600 g | Goiter, craniosynostosis, proptosis, advanced bone age, growth retardation, mental retardation | p.Ser505Asn | Antithyroid drugs | Holzapfel et al. [16] |
| Subtotal thyroidectomy | ||||||
| 3 | Newborn period | 39 wk/3,500 g | Poor weight gain, diarrhea, excessive sweating and irritability | p.Ala623Val | Antithyroid drugs | Aycan et al. [4] |
| 4 | Newborn period | 32 wk/1,660 g | Goiter, hyperactivity, mental retardation, advanced bone age | p.Phe631Leu | Antithyroid drugs | Kopp et al. [1] |
| Subtotal thyroidectomy | ||||||
| Radioiodine treatment | ||||||
| 5 | Newborn period | 36 wk/2,520 g | Craniosynostosis | p.Ser281Asn | Antithyroid drugs | Gr├╝ters et al. [14] |
| Total thyroidectomy | ||||||
| 6 | Newborn period | 34 wk/3,290 g | Tachycardia, tachypnea, craniosynostosis, dolichocephaly, advanced bone age, midface hypoplasia, proptosis | p.Ser281Asn | Antithyroid drugs | Chester et al. [13] |
| 7 | Newborn period | 32 wk/1,690 g | Goiter, proptosis, advanced bone age, hepatosplenomegaly, jaundice | p.Met453Thr | Antithyroid drugs | de Roux et al. [18] |
| 8 | Newborn period | 36 wk/3,040 g | Goiter, proptosis, advanced bone age, delayed pubertal and psychomotor development, mental retardation, splenomegaly | p.Met453Thr | Subtotal thyroidectomy | Lavard et al. [12] |
| Radioiodine treatment | ||||||
| 9 | Newborn period | 38 wk/2,600 g | Goiter, craniosynostosis, proptosis | p.Ser505Asn | Antithyroid drugs | Schwab et al. [15] |
| Total thyroidectomy | ||||||
| 10 | Newborn period | 37 wk/2,250 g | Goiter | p. Ala428Val | Antithyroid drugs | B├Črgel et al. [7] |
| 11 | Newborn period | 32 weeks/1,860 g | Goiter, craniosynostosis, advanced bone age | p.Leu512Gln | Antithyroid drugs | Nishihara et al. [8] |
| Radioiodine treatment | ||||||
| 12 | Newborn period | 35 wk/2,050 g | Goiter, advanced bone age, accelerated statural growth, speech disturbance, mental retardation, eyelid retraction | p.Ile568Thr | Antithyroid drugs | Tonacchera et al. [11] |
| 13 | Newborn period | 33 wk/1,450 g | Goiter, mental retardation, craniosynostosis, mild proptosis | p.Thr632Ile | Antithyroid drugs | Kopp et al. [10] |
| Subtotal thyroidectomy | ||||||
| Radioiodine treatment | ||||||
| 14 | Newborn period | 36 wk/2,040 g | Goiter, craniosynostosis, dolichocephaly, proptosis, hepatomegaly, periorbital edema, advanced bone age | p.Asp633Tyr | Antithyroid drugs | Bircan et al. [9] |
| Subtotal thyroidectomy (3 times) | ||||||
| 15 | Infancy | 37 wk/2,500 g | Goiter, advanced bone age | p.Val597Met | Antithyroid drugs | Esapa et al. [19] |
| Total thyroidectomy | ||||||
| 16 | Infancy | 40 wk/2,540 g | Goiter, advanced bone age, atopic dermatitis, growth retardation | p.Ser505Asn | Antithyroid drugs | Fuhrer et al. [20] |
| 17 | 14 Months | 40 wk/4,000 g | Diarrhea, increased growth velocity, advanced bone age | p.Pro639Ser | Antithyroid drugs | Agretti et al. [3] |
References
1. Kopp P, van Sande J, Parma J, Duprez L, Gerber H, Joss E, et al. Brief report: congenital hyperthyroidism caused by a mutation in the thyrotropin-receptor gene. N Engl J Med 1995;332:150ŌĆō4.


2. Gozu HI, Lublinghoff J, Bircan R, Paschke R. Genetics and phenomics of inherited and sporadic non-autoimmune hyperthyroidism. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2010;322:125ŌĆō34.


3. Agretti P, De Marco G, Biagioni M, Iannilli A, Marigliano M, Pinchera A, et al. Sporadic congenital nonautoimmune hyperthyroidism caused by P639S mutation in thyrotropin receptor gene. Eur J Pediatr 2012;171:1133ŌĆō7.


4. Aycan Z, A─¤lad─▒o─¤lu SY, Ceylaner S, Cetinkaya S, Ba┼¤ VN, Kendirici HN. Sporadic nonautoimmune neonatal hyperthyroidism due to A623V germline mutation in the thyrotropin receptor gene. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol 2010;2:168ŌĆō72.



5. van der Kaay DC, Wasserman JD, Palmert MR. Management of neonates born to mothers with Graves' disease. Pediatrics 2016;137.

6. de Roux N, Polak M, Couet J, Leger J, Czernichow P, Milgrom E, et al. A neomutation of the thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor in a severe neonatal hyperthyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1996;81:2023ŌĆō6.


7. B├Črgel K, Pohlenz J, Koch HG, Bramswig JH. Long-term carbimazole treatment of neonatal nonautoimmune hyperthyroidism due to a new activating TSH receptor gene mutation (Ala428Val). Horm Res 2005;64:203ŌĆō8.


8. Nishihara E, Fukata S, Hishinuma A, Kudo T, Ohye H, Ito M, et al. Sporadic congenital hyperthyroidism due to a germline mutation in the thyrotropin receptor gene (Leu 512 Gln) in a Japanese patient. Endocr J 2006;53:735ŌĆō40.


9. Bircan R, Miehle K, Mladenova G, Ivanova R, Ivanova R, Sarafova A, et al. Multiple relapses of hyperthyroidism after thyroid surgeries in a patient with long term follow-up of sporadic non-autoimmune hyperthyroidism. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 2008;116:341ŌĆō6.


10. Kopp P, Jameson JL, Roe TF. Congenital nonautoimmune hyperthyroidism in a nonidentical twin caused by a sporadic germline mutation in the thyrotropin receptor gene. Thyroid 1997;7:765ŌĆō70.


11. Tonacchera M, Agretti P, Rosellini V, Ceccarini G, Perri A, Zampolli M, et al. Sporadic nonautoimmune congenital hyperthyroidism due to a strong activating mutation of the thyrotropin receptor gene. Thyroid 2000;10:859ŌĆō63.


12. Lavard L, Sehested A, Brock Jacobsen B, Muller J, Perrild H, Feldt-Rasmussen U, et al. Long-term follow-up of an infant with thyrotoxicosis due to germline mutation of the TSH receptor gene (Met453Thr). Horm Res 1999;51:43ŌĆō6.


13. Chester J, Rotenstein D, Ringkananont U, Steuer G, Carlin B, Stewart L, et al. Congenital neonatal hyperthyroidism caused by germline mutations in the TSH receptor gene. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 2008;21:479ŌĆō86.




14. Gr├╝ters A, Sch├Čneberg T, Biebermann H, Krude H, Krohn HP, Dralle H, et al. Severe congenital hyperthyroidism caused by a germ-line neo mutation in the extracellular portion of the thyrotropin receptor. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1998;83:1431ŌĆō6.


15. Schwab KO, S├Čhlemann P, Gerlich M, Broecker M, Petrykowski W, Holzapfel HP, et al. Mutations of the TSH receptor as cause of congenital hyperthyroidism. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 1996;104 Suppl 4:124ŌĆō8.


16. Holzapfel HP, Wonerow P, von Petrykowski W, Henschen M, Scherbaum WA, Paschke R. Sporadic congenital hyperthyroidism due to a spontaneous germline mutation in the thyrotropin receptor gene. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1997;82:3879ŌĆō84.


17. Scaglia PA, Chiesa A, Bastida G, Pacin M, Domen├® HM, Gru├▒eiro-Papendieck L. Severe congenital nonautoimmune hyperthyroidism associated to a mutation in the extracellular domain of thyrotropin receptor gene. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol 2012;56:513ŌĆō8.



18. de Roux N, Misrahi M, Chatelain N, Gross B, Milgrom E. Microsatellites and PCR primers for genetic studies and genomic sequencing of the human TSH receptor gene. Mol Cell Endocrinol 1996;117:253ŌĆō6.









