|
 |
- Search
| Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab > Volume 19(1); 2014 > Article |
Abstract
A girl (age, 12 years 11 months) consulted the pediatric endocrinology clinic because of a rapidly growing right breast mass over 13 cm observed during the preceding 3 months. A surgical excision was performed, and the mass was diagnosed as a giant juvenile fibroadenoma. Giant juvenile fibroadenomas are rare, usually occurring between 10 and 18 years of age, and characterized by massive and rapid enlargement of an encapsulated mass. The etiology is believed to be an end-organ hypersensitivity to normal levels of estrogen. We report a case of giant juvenile fibroadenoma and present a review of the diagnostic workup and management of a large breast tumor during adolescence.
Breast masses are uncommon in children and adolescents. The majority of them are associated with inflammation due to infection or benign tumors like fibroadenomas1,2,3). Among those breast masses, some pathologic lesions such as giant fibroadenoma, phyllodes tumor, and virginal breast hypertrophy (juvenile macromastia) rapidly and massively increase in size over a short time period4,5). Fibroadenomas usually present as an encapsulated, monbile, rubbery, nontender mass. Giant fibroadenomas account for 0.5%-2% of all fibroadenomas and the exact etiology is not known. There are no clear-cut data on incidence of fibroadenoma in the general population. In one study, the rate of occurence of fibroadenoma in women was 7% to 13%. If the mass is not diagnosed early, it can cause psychological trauma to the patient and result in a very different prognosis6,7). Therefore, appropriate investigation and proper management at an early stage of illness is very important.
A girl (age, 12 years 11 months) presented with a giant juvenile fibroadenoma that occurred just after menarche and showed rapid growth over a short time period. Giant juvenile fibroadenoma is a rare variant of fibroadenoma with peak incidence occurring in late adolescence and predominately in African-American females8,9). We report a case of giant juvenile fibroadenoma with a mini-review of the literature related to diagnostic workup, differential diagnosis, and management.
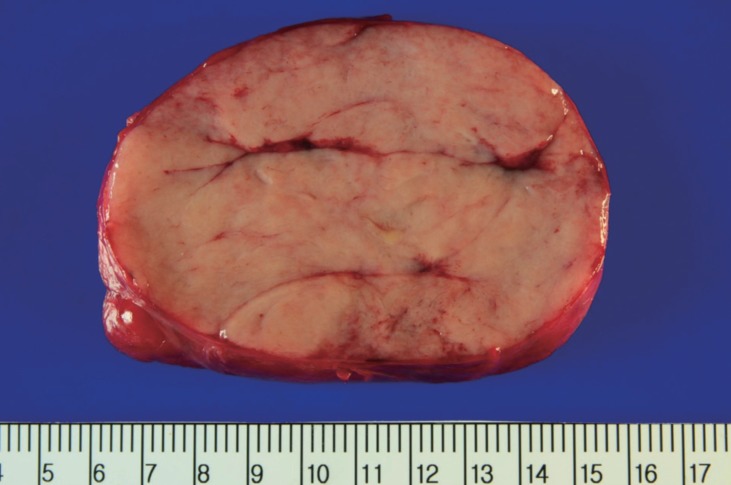
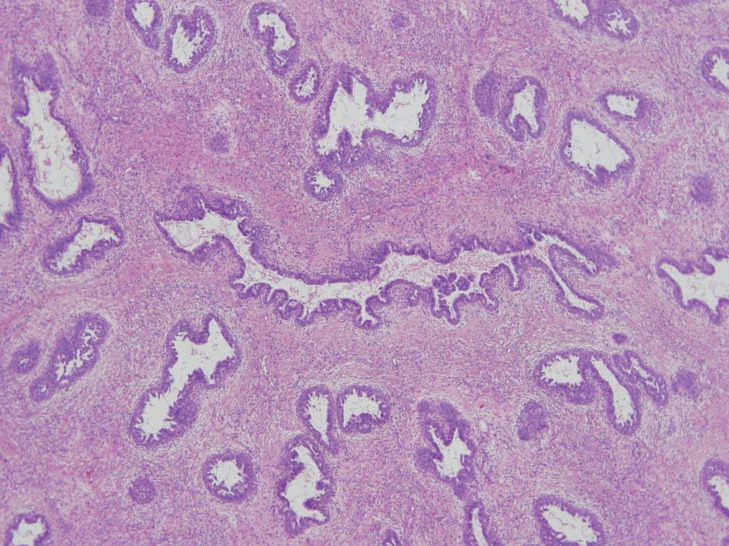
A girl (age, 12 years 11 months) presented with a rapidly enlarging and painful mass in the right breast that she noticed during the preceding 3 months. At the early stage she felt a difference in size of breasts and found nontender small breast lump in upper outer quadrant of the right breast but overlooked. She reached menarche a week prior to being seen at our clinic. There was no history of trauma, pyorrhea, lactorrhea, burning sensation, fever, fatigue, or weight loss. There were no significant familial diseases of the breast and no history of irradiation to the chest area. On physical examination, her weight and height were 46.4 kg and 159.6 cm; her calculated body mass index was 18.2 (25th-50th percentile). A 13 cm├Ś8 cm large mass was found in the right breast subareolar area, while the other breast was normal (Fig. 1). The mass was firm, round, and not fixed to the underlying structure. The overlying skin was tense and shiny with scattered redness and the veins in the skin were engorged. There was no skin dimple or ulceration and no lymph node enlargement in the axillary and supraclavicular regions. The laboratory test results including complete blood count and biochemical examination were within normal limits. The white blood cell count was 8.09├Ś103 cells/┬ĄL. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate was 4 mm/hr, and the C-reactive protein level was less than 0.1 mg/dL. The patient's chest radiograph was normal. Ultrasonography of the breast showed a giant encapsulated homogenous isoechoic mass occupying nearly the entire right breast (Fig. 2). She underwent a fine needle aspiration, and the pathologic finding was fibroadenoma. She then underwent total excision of the breast mass, conserving the normal breast tissue, nipple, and areola. The excised mass measured 10 cm├Ś9 cm├Ś5.5 cm and weighed 660 g (Fig. 3). The cut surface of the mass was tan colored and rounded with slit-like spaces. Histopathology showed increased cellularity stromal connective tissue, which surrounded the circumferential pattern of the ductules (pericanalicular type), and epithelial proliferation (Fig. 4). There was more stromal cellularity with a greater degree of epithelial hyperplasia than the usual type of fibroadenoma at low magnification. Prominently increased stromal cellularity was seen at high magnification. Although surgical excision with breast-conserving surgery was performed successfully, her mass recurred 6 months after surgery. 2.9-cm- and 1.2-cm-sized isoechoic nodules were found in upper inner quadrant and subareolar area in ultrasonogrphy. On 6 months later follow-up examination, they increased slightly to 4 cm and 1.7 cm. The patient underwent multiple excision of right breast nodules conserving the normal breast tissue, nipple and areola.
Giant juvenile fibroadenoma is a rare variant of fibroadenoma (0.5%-2% of all fibroadenomas) and is characterized by rapid growth. Peak incidence occurs in late adolescence, age 10 to 18 years, with African-American females at increased risk4,5). However, some giant fibroadenomas have been reported in Asia and recently in Korea6,7,8). The size of a giant juvenile fibroadenoma is usually more than 5 cm or more than 500 g. Many characteristics of giant juvenile fibroadenoma are typically considered indicators of malignancy4,5,9). The mass can compress adjacent tissue, distort lobular architecture, and create peau d'orange, nipple inversion, skin dimpling, or dilation of superficial veins. Therefore, a pathologic diagnosis is required in order to rule out malignant disease in these patients2,5,6,9). However, giant juvenile fibroadenoma is encapsulated and benign although the underlying mass may frequently recur and cause a major distortion to the breast contour3).
The exact etiology is unknown. Hormonal influences are thought to be a contributing factor. Excessive endogenous or exogenous estrogen stimulation, hypersensitivity of mammary gland tissue to local estrogen, and relative deficiency of estrogen antagonists such as progesterone, have been implicated in the pathogenesis because giant juvenile fibroadenomas increase in frequency during puberty or pregnancy and in response to oral contraceptives8,10,11).
Usually, adolescent breasts grow rapidly soon after the first menstrual period. A large breast mass might be one of three types: giant fibroadenoma, phyllodes tumor, and virginal breast hypertrophy (juvenile macromastia). Other less common causes are lipoma, mammary hamartoma, breast abscess, fibrocystic change, and adenocarcinoma. The differential diagnosis of a large breast mass in adolescent females is important for determining treatment modalities. In some cases, surgical resection is requested, while other cases may only require local excision, aspiration, or conservative therapy7,12).
In the diagnostic work-up, sonography and fine-needle aspiration are used after physical examination4,7,13). While it is easier to identify cell types and structures among malignant diseases and can obtain larger size of samples through core needle biopsy, fine needle aspiration biopsy is preferred since it is less invasive to patients and still can distinguish malignancy in young age group which is mostly comprised of benign diseases with large mass. Often other lesions can be ruled out by physical examination, sonography, and biopsy. Patients with phyllodes tumors are usually 40 to 50 years of age at the time of diagnosis. And heterogeneous echo patterns of the mass have been reported as one of the ultrasonography features of phyllodes tumors. Histologically, a phyllodes tumor is characterized by increased cellularity, frequent mitosis, leaf-like structure, and a lack of complete encapsulation. In contrast to a phyllodes tumor, giant juvenile fibroadenomas are characterized by a well-defined capsule and the lack of leaf-like structures7,12). About 90% of the tumors are low grade or benign. In low-grade phyllodes tumors, there are prominent leaf-like structures and characteristic stromal condensation around the ducts, and it infiltrates the surrounding breast tissue with mitotic figures (<4/high power field [HPF]). In high-grade phyllodes tumor, there is stromal overgrowth with atypia and atypical mitotic figures (<10/HPF)12). In virginal breast hypertrophy, there is rapid growth of one or both breasts, which is often asymmetrical and occasionally accompanied by erythematous, itchy, and painful lesions. Histologically, there is abundant connective tissue and duct proliferation, frequently with epithelial hyperplasia but little or no lobule formation7,12).
Giant lipoma is soft and movable showing nodules of mature adipose tissue with a well-defined capsule on ultrasound. Breast abscesses develop suddenly, and are usually painful and accompanied with fluctuation and erythema. Hamartomas show sharp margin multilobular structures and fibrous components with a heterogeneous internal echo pattern on ultrasound13).
Most fibroadenomas tend to grow slowly and remain static for months or years. They often lose their cellularity with aging. The overall rate of complete regression of a clinically detectable breast mass in an adolescent is between 10% and 40%. Regression may occur due to infarction with calcification and hyalinization14,15). Therefore, conservative monitoring with a 3 to 4 month interval is reasonable for small fibroadenomas. However, surgical excision is indicated in the following case to conserve the breast: a rapidly growing mass, a mass over 5 cm in diameter, a mass causing distortion of breast architecture or with overlying skin changes, and symptoms and signs indicating malignancy15). Malignant change of a fibroadenoma is less than 0.3%16). However, the recurrence rate is about 33% at the 5-year follow-up after excision17).
Recently, female adolescents with a breast problem often come to the pediatric endocrinology clinic. Thus, it is essential for pediatric endocrinologist to know the diagnostic workup, differential diagnosis, and management of breast masses that can occur in female adolescents.
References
1. Boothroyd A, Carty H. Breast masses in childhood and adolescence: a presentation of 17 cases and a review of the literature. Pediatr Radiol 1994;24:81ŌĆō84. PMID: 8078727.


2. Neinstein LS. Breast disease in adolescents and young women. Pediatr Clin North Am 1999;46:607ŌĆō629. PMID: 10384810.


3. Fallat ME, Ignacio RC Jr. Breast disorders in children and adolescents. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol 2008;21:311ŌĆō316. PMID: 19064223.


4. Park CA, David LR, Argenta LC. Breast asymmetry: presentation of a giant fibroadenoma. Breast J 2006;12:451ŌĆō461. PMID: 16958965.


5. Ugburo AO, Olajide TO, Fadeyibi IO, Mofikoya BO, Lawal AO, Osinowo AO. Differential diagnosis and management of giant fibroadenoma: comparing excision with reduction mammoplasty incision and excision with inframammary incision. J Plast Surg Hand Surg 2012;46:354ŌĆō358. PMID: 22998148.


6. Lee CJ, Kim YJ, Seo YT, Pak SJ, Lee SI. Treatment of multiple bilateral juvenile fibroadenomas in a teenage breast by central pedicle breast reduction, with vertical and short horizontal scar: case report. Aesthetic Plast Surg 2004;28:228ŌĆō230. PMID: 15599536.


7. Nikumbh DB, Desai SR, Madan PS, Patil NJ, Wader JV. Bilateral giant juvenile fibroadenomas of breasts:a case report. Patholog Res Int 2011;2011:482046. PMID: 21660274.




8. Tochika N, Ogawa Y, Kumon M, Araki K, Sugimoto T, Ohtsuki Y, et al. Rapid growing fibroadenoma in an adolescent. Breast Cancer 1998;5:321ŌĆō324. PMID: 18841338.

9. Anavi BL, Mishev GG, Ivanov GP. Giant fibroadenoma of the breasts. Folia Med (Plovdiv) 2002;44:50ŌĆō52. PMID: 12751688.
10. Musio F, Mozingo D, Otchy DP. Multiple, gi ant fibroadenoma. Am Surg 1991;57:438ŌĆō441. PMID: 1647714.

11. Rao BR, Meyer JS, Fry CG. Most cystosarcoma phyllodes and fibroadenomas have progesterone receptor but lack estrogen receptor: stromal localization of progesterone receptor. Cancer 1981;47:2016ŌĆō2021. PMID: 6261932.


12. Juan R. Breast. Juan Ret al., editors. Rosai and Ackerman's surgical pathology. 9th ed. Philadelphia: Mosby.
13. Vade A, Lafita VS, Ward KA, Lim-Dunham JE, Bova D. Role of breast sonography in imaging of adolescents with palpable solid breast masses. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2008;191:659ŌĆō663. PMID: 18716091.


14. Neinstein LS, Atkinson J, Diament M. Prevalence and longitudinal study of breast masses in adolescents. J Adolesc Health 1993;14:277ŌĆō281. PMID: 8347638.


15. Jayasinghe Y, Simmons PS. Fibroadenomas in adolescence. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol 2009;21:402ŌĆō406. PMID: 19606032.


16. Ozzello L, Gump FE. The management of patients with carcinomas in fibroadenomatous tumors of the breast. Surg Gynecol Obstet 1985;160:99ŌĆō104. PMID: 2982218.

17. Grady I, Gorsuch H, Wilburn-Bailey S. Long-term outcome of benign fibroadenomas treated by ultrasound-guided percutaneous excision. Breast J 2008;14:275ŌĆō278. PMID: 18397185.


Fig.┬Ā1
Gross appearance of the right breast. The overlying skin has a shiny, tense appearance with vein engorgement.
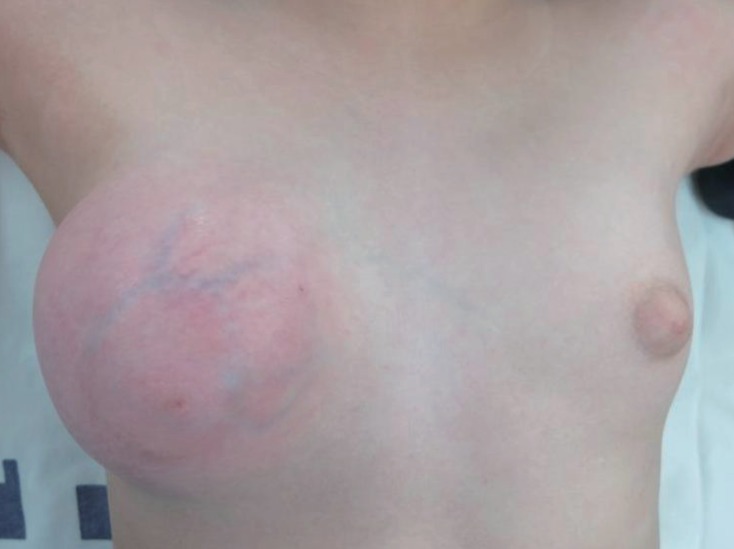
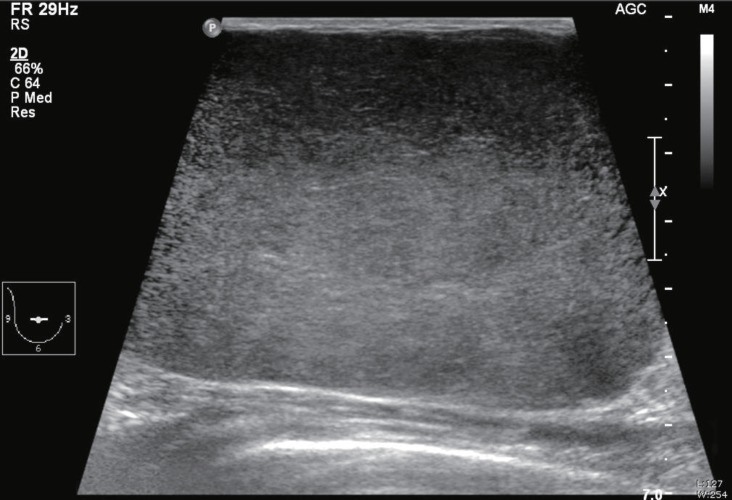
Fig.┬Ā2
An ultrasonogram showing a well capsulated giant homogeneous isoechoic mass occupying entire right breast.
- TOOLS
-
METRICS

-
- 24 Crossref
- 14,639 View
- 180 Download
- Related articles in APEM