 |
 |
- Search
| Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab > Volume 25(1); 2020 > Article |
|
Abstract
Patients with neurological disorders are at high risk of developing osteoporosis, as they possess multiple risk factors leading to low bone mineral density. Such factors include inactivity, decreased exposure to sunlight, poor nutrition, and the use of medication or treatment that can cause lower bone mineral density such as antiepileptic drugs, ketogenic diet, and glucocorticoids. In this article, mechanisms involved in altered bone health in children with neurological disorders and management for patients with epilepsy, cerebral palsy, and Duchenne muscular dystrophy regarding bone health are reviewed.
Osteoporosis is an important comorbidity in children with genetic disorders predisposing to bone fragility and children with acute and chronic illnesses [1]. Osteoporosis in children results from inadequate bone accrual due to diminished rates of bone mineral deposition, whereas osteoporosis in adults primarily occurs from bone mineral loss [2]. Bone mineralization occurs throughout childhood and peaks at the end of adolescence, and the bone mineral density (BMD) achieved during childhood and adolescence determines the risk for osteoporosis and fractures during adulthood [3]. Children lacking adequate bone accretion are at higher risk of developing both fragility fractures during childhood and involutional osteoporosis as adults [4].
Children with neurological disorders such as epilepsy, cerebral palsy (CP), and Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) are at higher risk of low BMD and associated osteoporosis and fractures [5-7]. Pediatric neurological disorders constitute a major secondary cause of osteoporosis in children, as shown in Table 1, and account for a significant portion of the children who are referred for bone density assessment [1,8,9]. In this article, we review the risk factors of low BMD in children with neurological disorders in relation to bone physiology, with a focus on epilepsy, CP, and DMD, and discuss recent developments in management of bone health in these children.
The rates of bone absorption and deposition are equal in nongrowing bones, and this balance is maintained through the activities of osteoblasts and osteoclasts, respectively [2]. There is continual bone formation and absorption in living bones, with 4% and 1% of living bone surfaces harboring active osteoblasts and osteoclasts, respectively, at any given time [2]. The balance shifts toward increased bone formation in direct proportion to the amount of stress placed on the bone, with bone mass increasing in response to heavy impacts or loads [2]. As a result, healthy load-bearing bones gain adequate strength to carry heavy loads without risk of fragility fractures [10].
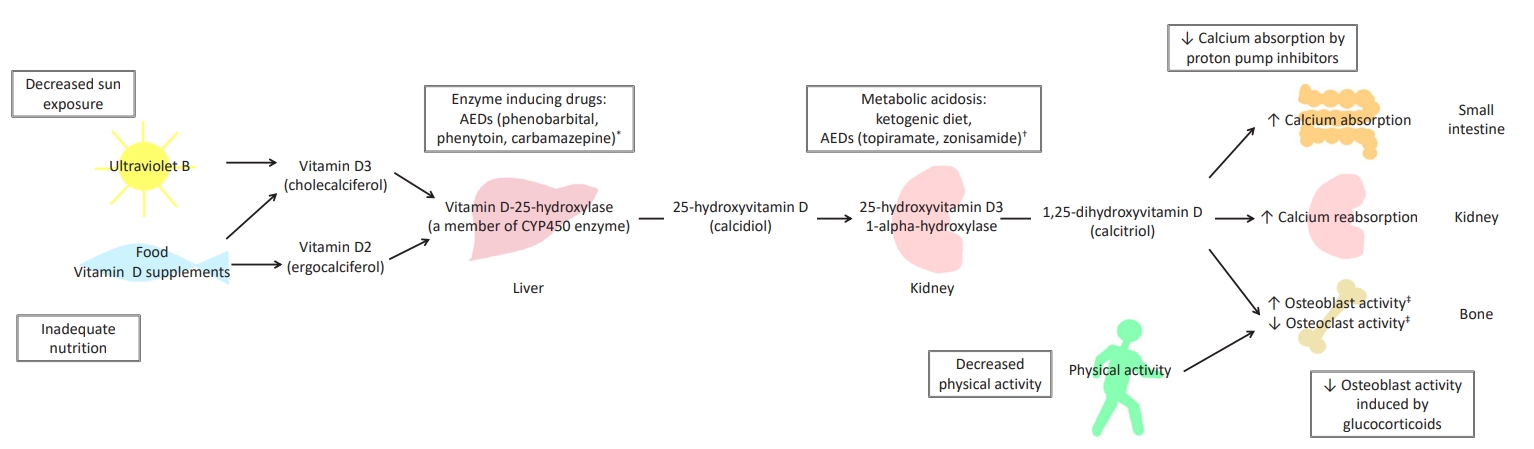
Calcium and vitamin D play critical roles in mineralization of bone. Most vitamin D is produced naturally in the skin from exposure to sunlight, and less than 10% is obtained orally from consumption of vitamin D-rich foods, such as oily fish (e.g., salmon, mackerel) or supplements (e.g., fish liver oils) [11,12]. The vitamin D produced from sunlight or digestively absorbed is biologically inert and requires activation by two sequential hydroxylation reactions, the first occurring in the liver and the second in the kidneys. In the liver, vitamin D-25-hyroxylase, a cytochrome P450 enzyme, converts vitamin D to 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) (i.e., calcidiol), and this compound is subsequently converted in the kidneys by 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 1-alpha-hydroxylase to 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D (1,25(OH)2D) (i.e., calcitriol); it is this final form that is biologically active (Fig. 1) [13,14].
Vitamin D plays a role in bone mineralization by maintaining adequate serum levels of calcium and phosphorus, which allow osteoblasts to build bone matrix [2]. The active form of vitamin D promotes calcium and phosphorus absorption in the small intestine, calcium reabsorption in the kidneys, increased osteoblast activity, and reduced osteoclast activity [13]. However, 1,25(OH)2D can also enhance bone resorption in the presence of reduced calcium balance [13]. Parathyroid hormone (PTH) regulates production of 1,25(OH)2D in a manner dependent on serum calcium level, as it promotes tubular reabsorption of calcium, increases renal excretion of phosphorus, and stimulates further production of 1,25(OH)2D [15,16].
Proper bone growth in an individual necessitates sufficient calcium consumption. Calcium is required for adequate mineralization of bone matrix, and a positive correlation exists between calcium intake and bone mass in individuals of all ages [17,18]. The recommended dietary calcium intake levels in children are 200 mg/day for ages 0ŌĆō6 months, 260 mg/day for ages 7ŌĆō12 months, 700 mg/day for ages 1ŌĆō3 years, 1,000 mg/day for ages 4ŌĆō8 years, and 1,300 mg/day for ages 9ŌĆō18 years [19]. Vitamin D is important for calcium absorption, and vitamin D deficiency results in bone demineralization [7]. The major source of vitamin D is obtained by synthesis in the skin from sun exposure, but dietary intake is also important [20]. A serum 1,25(OH)2D concentration of 70ŌĆō80 nmol/L is generally required to maintain bone health and reduce bone fragility [21]. Vitamin D deficiency also causes muscle weakness, which can be a substantial problem in children with neurological disorders [22,23]. The optimal doses of supplemented vitamin D for children with motor disabilities and generally low serum 1,25(OH)2D concentration are unknown, but vitamin D supplementation at 400 IU/day during infancy and 600ŌĆō1,000 IU/day during childhood may be needed to prevent secondary osteoporosis [6,19,24,25].
Children with neurological disorders are at greater risk of poor nutritional intake of calcium and vitamin D; furthermore, problems related to nutrition, such as malnutrition, food intolerance, swallowing problems, gastrointestinal reflux, constipation, eating disorders, and drug-nutrient interactions, are more common in these children [26,27].
The bone is sensitive to external stimuli and is highly responsive to the mechanical stresses exerted by gravity and muscle contractions [28]. This mechanical loading is necessary to stimulate bone deposition and to maintain skeletal integrity [28]. The forces applied on bones by daily physical activities induce bone remodeling, and this response increases the strength of the bones to endure these stresses [10]. Conversely, inactivity, low muscle support, and conditions of weightlessness have negative effects on bone integrity and cause loss of bone density [28,29], as immobilization and non-weight-bearing situations cause increased osteoclastic activity and cytokine production that results in reduced trabecular formation and thinning of long bone cortices [30].
Children with physical disabilities involving limited ambulation and reduced muscle mass, for example, patients with CP or neuromuscular disease, have lower BMD than healthy children [7,31]. These children can also face a major complication of repeated acute or temporary immobilization following orthopedic surgery or casting to treat fragility fractures; such immobilization causes further reduction in BMD and perpetuates a vicious cycle [32]. Hip casting in children with CP is associated with increased risk of future fracture, and even normal children suffering uncomplicated lower limb fractures casted for more than four weeks have been shown to acquire small, persistent deficits in bone density [33-36]. Separately, adolescents with epilepsy and lacking major motor or sensory impairments were shown to engage in fewer physical activities than sibling controls [37].
In addition to the direct effects of reduced mechanical stress on bone health, the reduced physical activity of children with neurological disorders results in less time spent outdoors, decreased exposure to sunlight, and, consequently, reduced vitamin D synthesis [6].
Several medications commonly used in children with neurological disorders have negative effects on bone health (Table 2). Glucocorticoid treatment is a main therapy in patients with DMD, and glucocorticoids are also used as antiseizure medications. Glucocorticoids impair differentiation of mesenchymal cells into osteoblasts and stimulate an increase in apoptosis of mature osteoblasts, resulting in a decrease in total osteoblast number [38]. In this way, glucocorticoids reduce the function of osteoblasts directly and indirectly by inhibiting expression of insulin-like growth factor I [38]. Glucocorticoids cause an initial increase in osteoclastogenesis but eventually cause a decrease in osteoclastogenesis due to reduced osteoblastic signals [38]. In summary, acute exposure to glucocorticoids enhances bone resorption, and prolonged exposure causes decreased bone remodeling, low BMD, and long-term increased fracture risk [38].
Antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) also have adverse effects on bone health. Inducers of the cytochrome P450 (CYP450) family of enzymes, (i.e., enzyme-inducing AEDs), such as phenobarbital, phenytoin, primidone, and carbamazepine, activate the CYP450 pathway, leading to accelerated vitamin D metabolism with resultant low serum 1,25(OH)2D level, elevated bone turnover, and secondary hyperparathyroidism [39,40]. However, CYP450 enzyme inhibitors such as valproic acid are also associated with low BMD, indicating that activation of the CYP450 pathway and the resultant reduction in vitamin D level is not the only mechanism underlying the AED-associated decrease in BMD [41].
Several studies have shown that benzodiazepines, such as diazepam, lorazepam, midazolam, and clonazepam, are associated with reduced BMD, reduced 1,25(OH)2D level, and increased alkaline phosphatase (ALP) level [42,43]. The overall levels of calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, and PTH were not affected [42,43]. However, these results remain controversial [44,45].
Phenobarbital is an enzyme-inducing AED that causes induction of hepatic microsomal enzymes, resulting in increased 1,25(OH)2D catabolism and osteomalacia [42,46]. Phenobarbital is also associated with direct inhibition of intestinal calcium absorption [47].
Phenytoin is another enzyme-inducing AED and has been reported to be associated with hypocalcemia, hypophosphatemia, the direct inhibition of intestinal calcium absorption [41,48,49].) Phenytoin also inhibited the cellular response and impaired the osteoblastic response to PTH [50,51]. Both primary and secondary hyperparathyroidism were observed in patients receiving phenytoin, and both conditions can result in increased bone resorption [52,53]. However, phenytoin has also been demonstrated to inhibit proliferation of human osteoblast-like cells, suggesting a direct effect on bone metabolism [51,54,55]. Finally, phenytoin exerts an inhibitory effect on calcitonin secretion, resulting in calcitonin deficiency [56,57].
Carbamazepine, another enzyme-inducing AED, causes decreased serum level of 1,25(OH)2D via increased 1,25(OH)2D catabolism, secondary hyperparathyroidism, and increased bone turnover [41]. Carbamazepine also directly inhibits human osteoblast-like cells, causing reduced bone cell proliferation [54], and directly inhibits intestinal calcium transport, although it does so through a vitamin D-independent mechanism [58].
Long-term use of valproic acid has been shown to be associated with low BMD in a dose-responsive manner [41]. The effect of valproic acid on BMD cannot be explained by altered vitamin D metabolism alone, as valproic acid is not an inducer of the CYP450 system but an inhibitor. Instead, valproic acid is believed to lower BMD through stimulation of osteoclast activity, causing an imbalance that contributes to bone loss [59]. However, reports on the mechanisms by which valproic acid causes low BMD show conflicting results. Some studies showed that serum 1,25(OH)2D level was within the normal range, whereas others found low 1,25(OH)2D level [52,60-67]. In most of the studies, serum PTH level was within the normal range; however, in a few studies, a marked increase in PTH level was observed [52,60-62,64-66,68-70]. The results regarding ALP and osteocalcin levels also differed among studies [59,61,62,65,69,71-74]. Valproic acid was not associated with abnormalities in serum calcium or phosphorus level in most of the studies [62,65,66,68,71,75].
The effects of newer AEDs on BMD have not been sufficiently studied. Based on a few studies, lamotrigine and levetiracetam do not seem to be associated with low BMD, whereas an association with low BMD does appear to exist for oxcarbazepine, topiramate, and zonisamide [41]. However, further studies are needed. One mechanism that has been proposed to explain the effects of 2 carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, namely, topiramate and zonisamide, on low BMD is medicationinduced chronic metabolic acidosis that leads to decreased absorption of vitamin D and consequent activation of PTH [6].
A ketogenic diet is a dietary treatment used to control seizures in epilepsy patients who are resistant to drug therapies. The classic ketogenic diet uses a 4:1 or 3:1 ratio of fat to nonfat, as measured in grams, such that approximately 80%ŌĆō90% of the total energy (calorie) obtained from food comes from fat. Patients on a ketogenic diet have been shown to have low BMD, and there was a significant association between low BMD and duration of dietary therapy [76]. Ketogenic diet-induced ketosis causes a chronic ketoacidotic state, which leads to decreased absorption of vitamin D, secondary activation of PTH, and increased bone resorption [6]. The high incidence of renal calculi and the elevated urine calcium:creatinine ratio observed in patients on a ketogenic diet also indicate a major effect of the ketogenic diet on calcium metabolism [76].
More than 50% of patients with epilepsy have low BMD, and the frequency of fractures in pediatric epilepsy patients is 2 to 3 times higher than that in children without epilepsy [77-80]. The low BMD in epilepsy patients is due to inactivity resulting from comorbidities such as CP or from epilepsy itself, decreased exposure to sunlight resulting from inactivity, and use of AEDs that lower BMD.
Despite the accepted association between epilepsy and low BMD, especially with regard to the impact of AEDs on BMD, not all epileptologists routinely screen for bone health [6,81]. A study showed that only 41% of pediatric neurologists and 28% of adult neurologists routinely evaluate bone health in epilepsy patients taking AEDs, suggesting a need for increased awareness [81].
There are currently no guidelines regarding management of bone health in pediatric epilepsy patients taking AEDs. However, some authors recommend screening serum 1,25(OH)2D level in these patients at least once per year, with more frequent (i.e., monthly) screening if abnormal 1,25(OH)2D level is detected [6,16]. In patients at higher risk of abnormal bone health, such as those who take AEDs known to adversely affect BMD, evaluations of other markers, such as serum calcium, phosphorus, PTH, and ALP levels, should be considered [6]. The specific indications for dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scans in pediatric epilepsy patients have not yet been established. However, as current recommendations for DXA scans include patients at high risk for low bone density, DXA scans should also be considered for epilepsy patients who are a high-risk for low bone density score [82].
According to the guideline for management of children on ketogenic diets, serum vitamin D level, along with other markers, should be assessed before starting ketogenic dietary therapy and routinely thereafter, specifically, at 1, 3, 6, 9, and 12 months during the first year and every 6 months for the duration of the diet [83]. A DXA scan is also recommended for all patients after 2 years on a ketogenic diet [83]. Administration of calcium and vitamin D supplements is recommended for all patients, and higher doses of vitamin D supplementation are recommended for patients with low vitamin D level [83].
A study showed that 77% of children with moderate to severe CP and 97% of non-ambulatory children had osteopenia, which is defined as a femoral BMD z-score less than -2.0 [5]. In a large population study of 763 children with CP, fracture prevalence was 12%, and more than 70% of fractures occurred in lower limb bones [84].
The cause of low BMD in CP patients is likely multi-factorial. The contributing mechanical factors include limitation of weight-bearing ambulation and a higher incidence of temporary immobilization associated with orthopedic surgery, which occurs commonly in pediatric CP patients [5]. Outdoor activities are also significantly limited in CP patients, resulting in decreased exposure to sunlight and consequent low serum vitamin D level [5]. Oral-motor dysfunction can increase feeding difficulties in children with CP, and this can lead to poor nutrition and low calcium intake [85]. Many children with CP have comorbid epilepsy and take AEDs that often have adverse effects on bone health [5]. In addition to AEDs, the proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) that are widely used in children with CP because of dyspepsia or gastroesophageal reflux also have a negative effect on BMD, as they decrease calcium and magnesium absorption [7]. CP is also often associated with premature birth, and rickets of prematurity occurs more frequently in CP patients [5].
A guideline for children with CP at risk of osteoporosis recommends the following for all patients: routine evaluations for serum 1,25(OH)2D level and urine calcium/osmolality ratio, maintenance of adequate calcium intake and vitamin D supplementation, and encouragement of weight-bearing activities through physiotherapies [86,87]. In CP patients with osteoporosis who have suffered fragility fractures or bone pain, additional tests including analysis of serum calcium, phosphorus, PTH, and ALP levels; lateral spine and wrist X-rays; and DXA scans are indicated, and bisphosphonate therapy should be considered [86,87].
Boys with DMD who are treated with glucocorticoids frequently develop osteoporosis, which manifests as fragility fractures of vertebrae or long bones [88]. Approximately 20%ŌĆō60% of boys with DMD experience low-trauma extremity fractures, and 30% experience symptomatic vertebral fractures [88-90]. As vertebral fractures are frequently asymptomatic, their prevalence may be higher than indicated in these previous reports [91].
The main risk factors of osteoporosis in patients with DMD are progressive myopathy causing muscle mass loss, muscle weakness, and inactivity or immobilization and use of glucocorticoids [92]. Glucocorticoids are a main therapy in boys with DMD; administration is started when the patient reaches the plateau phase of motor skills, usually at 4ŌĆō8 years of age, is maintained continuously for the life of the patient [93]. There have been several studies suggesting that deflazacort has fewer adverse effects on BMD than does prednisolone or methylprednisone, but other studies have been unable to confirm the potential bone-sparing effects of deflazacort [94-98].
A guideline for management of DMD patients suggests the following: (1) monitoring the presence of back pain or fractures at each visit, (2) analyzing serum calcium, phosphate, magnesium, ALP, and PTH levels at baseline, (3) baseline and subsequent annual monitoring of calcium/vitamin D intake, serum 1,25(OH)2D level, and DXA scans, and (4) lateral spine X-rays at baseline and again every 1 to 2 years thereafter if the patient is on steroids or every 2 to 3 years thereafter if not on steroids [91]. Then, if clinically significant bone fragility develops, maintenance of adequate calcium and vitamin D intake and treatment with bisphosphonate therapy are recommended. Further, DXA scans and monitoring of serum 1,25(OH)2D level, back pain occurrence, and other bone metabolism biomarkers every six months should be conducted, as well as annual spine X-rays [91].
In conclusion, many children with neurological diseases are at risk of developing osteoporosis, as they possess multiple risk factors leading to low BMD, including inactivity, decreased exposure to sunlight, poor nutrition, and use of medication or treatment that can lower BMD (e.g., AEDs, glucocorticoids, PPIs, ketogenic diet). Awareness of the increased risk of osteoporosis in these children and routine monitoring for bone health are important, as adequate management is only possible by assuring sufficient calcium and vitamin D intake and providing appropriate physiotherapy or bisphosphonate therapy.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This study was supported by a 2019 research grant from Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital.
Fig.┬Ā1.
Vitamin D, bone metabolism, and alteration in patients with neurological disorders. Boxed phrases refer to factors that can cause osteoporosis in patients with neurological disorders. * CYP450 enzyme-inducing drugs increase the metabolism of vitamin D resulting in decreased serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D level and subsequently decreased serum 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D (1,25(OH)2D) level. ŌĆĀ Ketogenic diet and other drugs that induce metabolic acidosis cause hypercalciuria in association with calcium loss from bone, resulting in negative calcium balance. Ketogenic diet can also cause inadequate calcium and vitamin D intake. ŌĆĪ Such a phenomenon is observed in a setting with normal serum calcium level. In the presence of low serum calcium level, 1,25(OH)2D induces bone resorption. AEDs, antiepileptic drugs.
Table┬Ā1.
Table┬Ā2.
Osteoporosis monitoring and management for patients with neurological disorders
| Disease | Monitoring | Management | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epilepsy* | ŌĆó | Serum 1,25(OH)2D level at least once a year | ŌĆó | Ensure adequate calcium/vitamin D intake |
| ŌĆó | Serum calcium, phosphorus, PTH, and ALP levels, and DXA scans in patients with higher risk (e.g., who take AEDs) | ŌĆó | Calcium and vitamin D supplements for all patients on ketogenic diet | |
| ŌĆó | Serum 1,25(OH)2D level at 1, 3, 6, 9, and 12 months during the first year and then every 6 months, and DXA scan after 2 years in patients on ketogenic diet | ŌĆó | Consider bisphosphonate therapy in patients with osteoporosis | |
| CP8 [7] | ŌĆó | Serum 1,25(OH)2D level and urine calcium/osmolality ratio 1ŌĆō2 times a year | ŌĆó | Ensure adequate calcium/vitamin D intake |
| ŌĆó | Serum calcium, phosphorus, PTH, ALP, and creatinine levels, X-rays of symptomatic area and/or lateral spine X-ray, DXA scan for patients with osteoporosis (fragility fracture and/or bone pain) | ŌĆó | Consider bisphosphonate therapy in patients with osteoporosis | |
| DMD [91] | ŌĆó | Presence of back pain or fractures at every clinical visit. | ŌĆó | Ensure adequate calcium/vitamin D intake |
| ŌĆó | Serum calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, ALP, PTH at baseline only (follow-up as appropriate) | ŌĆó | Verify normal renal function | |
| ŌĆó | Serum 1,25(OH)2D level and DXA scan at baseline and annually | ŌĆó | Consider bisphosphonate therapy in patients with osteoporosis | |
| ŌĆó | Lateral spine X-ray at baseline and every 1ŌĆō2 years if on steroids, and every 2ŌĆō3 years if not on steroids | |||
References
1. Ward LM, Konji VN, Ma J. The management of osteoporosis in children. Osteoporos Int 2016;27:2147ŌĆō79.



2. Houlihan CM, Stevenson RD. Bone density in cerebral palsy. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am 2009;20:493ŌĆō508.



3. Bonjour JP, Theintz G, Buchs B, Slosman D, Rizzoli R. Critical years and stages of puberty for spinal and femoral bone mass accumulation during adolescence. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1991;73:555ŌĆō63.



4. Melton LJ 3rd, Kan SH, Wahner HW, Riggs BL. Lifetime fracture risk: an approach to hip fracture risk assessment based on bone mineral density and age. J Clin Epidemiol 1988;41:985ŌĆō94.


5. Henderson RC, Lark RK, Gurka MJ, Worley G, Fung EB, Conaway M, et al. Bone density and metabolism in children and adolescents with moderate to severe cerebral palsy. Pediatrics 2002;110(1 Pt 1):e5.

6. McNamara NA, Romanowski EMF, Olson DP, Shellhaas RA. Bone health and endocrine comorbidities in pediatric epilepsy. Semin Pediatr Neurol 2017;24:301ŌĆō9.


7. Yasar E, Adiguzel E, Arslan M, Matthews DJ. Basics of bone metabolism and osteoporosis in common pediatric neuromuscular disabilities. Eur J Paediatr Neurol 2018;22:17ŌĆō26.


8. Gordon CM, Leonard MB, Zemel BS. 2013 Pediatric Position Development Conference: executive summary and reflections. J Clin Densitom 2014;17:219ŌĆō24.


9. Jones AR, Zacharin MR, Cameron FJ, Simm PJ. Bone density assessment in a tertiary paediatric centre over 13 years: referral patterns and limitations. J Paediatr Child Health 2015;51:608ŌĆō13.


10. Frost HM. Bone's mechanostat: a 2003 update. Anat Rec A Discov Mol Cell Evol Biol 2003;275:1081ŌĆō101.


11. DeLuca HF. Overview of general physiologic features and functions of vitamin D. Am J Clin Nutr 2004;80(6 Suppl):1689SŌĆō1696S.


12. Misra M, Pacaud D, Petryk A, Collett-Solberg PF, Kappy M. Vitamin D deficiency in children and its management: review of current knowledge and recommendations. Pediatrics 2008;122:398ŌĆō417.


13. Holick MF, Binkley NC, Bischoff-Ferrari HA, Gordon CM, Hanley DA, Heaney RP, et al. Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2011;96:1911ŌĆō30.


16. Shellhaas RA, Joshi SM. Vitamin D and bone health among children with epilepsy. Pediatr Neurol 2010;42:385ŌĆō93.


17. Mesias M, Seiquer I, Navarro MP. Calcium nutrition in adolescence. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2011;51:195ŌĆō209.


18. Blair HC, Robinson LJ, Huang CL, Sun L, Friedman PA, Schlesinger PH, et al. Calcium and bone disease. Biofactors 2011;37:159ŌĆō67.



19. Ross AC, Manson JE, Abrams SA, Aloia JF, Brannon PM, Clinton SK, et al. The 2011 report on dietary reference intakes for calcium and vitamin D from the Institute of Medicine: what clinicians need to know. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2011;96:53ŌĆō8.


20. Cheng JB, Levine MA, Bell NH, Mangelsdorf DJ, Russell DW. Genetic evidence that the human CYP2R1 enzyme is a key vitamin D 25-hydroxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2004;101:7711ŌĆō5.



21. Dawson-Hughes B, Heaney RP, Holick MF, Lips P, Meunier PJ, Vieth R. Estimates of optimal vitamin D status. Osteoporos Int 2005;16:713ŌĆō6.



22. Soderpalm AC, Magnusson P, Ahlander AC, Karlsson J, Kroksmark AK, Tulinius M, et al. Low bone mineral density and decreased bone turnover in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Neuromuscul Disord 2007;17:919ŌĆō28.


23. Francis RM, Anderson FH, Patel S, Sahota O, van Staa TP. Calcium and vitamin D in the prevention of osteoporotic fractures. Qjm 2006;99:355ŌĆō63.



24. Kilpinen-Loisa P, Pihko H, Vesander U, Paganus A, Ritanen U, Makitie O. Insufficient energy and nutrient intake in children with motor disability. Acta Paediatr 2009;98:1329ŌĆō33.


25. Mutlu GY, Kusdal Y, Ozsu E, Cizmecioglu FM, Hatun S. Prevention of Vitamin D deficiency in infancy: daily 400 IU vitamin D is sufficient. Int J Pediatr Endocrinol 2011;2011:4.




26. Gonzalez L, Nazario CM, Gonzalez MJ. Nutrition-related problems of pediatric patients with neuromuscular disorders. P R Health Sci J 2000;19:35ŌĆō8.

27. Aydin K, Kartal A, Keles Alp E. High rates of malnutrition and epilepsy: two common comorbidities in children with cerebral palsy. Turk J Med Sci 2019;49:33ŌĆō7.



29. Frost HM, Schonau E. The "muscle-bone unit" in children and adolescents: a 2000 overview. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 2000;13:571ŌĆō90.



30. Zacharin M. Current advances in bone health of disabled children. Curr Opin Pediatr 2004;16:545ŌĆō51.


31. Mergler S, Evenhuis HM, Boot AM, De Man SA, Bindels-De Heus KG, Huijbers WA, et al. Epidemiology of low bone mineral density and fractures in children with severe cerebral palsy: a systematic review. Dev Med Child Neurol 2009;51:773ŌĆō8.


32. Zacharin M. Assessing the skeleton in children and adolescents with disabilities: avoiding pitfalls, maximising outcomes. A guide for the general paediatrician. J Paediatr Child Health 2009;45:326ŌĆō31.


33. Henderson RC. Bone density and other possible predictors of fracture risk in children and adolescents with spastic quadriplegia. Dev Med Child Neurol 1997;39:224ŌĆō7.


34. Sturm PF, Alman BA, Christie BL. Femur fractures in institutionalized patients after hip spica immobilization. J Pediatr Orthop 1993;13:246ŌĆō8.

35. Stasikelis PJ, Lee DD, Sullivan CM. Complications of osteotomies in severe cerebral palsy. J Pediatr Orthop 1999;19:207ŌĆō10.


36. Henderson RC, Kemp GJ, Campion ER. Residual bonemineral density and muscle strength after fractures of the tibia or femur in children. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1992;74:211ŌĆō8.


37. Wong J, Wirrell E. Physical activity in children/teens with epilepsy compared with that in their siblings without epilepsy. Epilepsia 2006;47:631ŌĆō9.


38. Canalis E. Mechanisms of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2003;15:454ŌĆō7.


39. Verrotti A, Greco R, Morgese G, Chiarelli F. Increased bone turnover in epileptic patients treated with carbamazepine. Ann Neurol 2000;47:385ŌĆō8.


40. Nicholas JM, Ridsdale L, Richardson MP, Grieve AP, Gulliford MC. Fracture risk with use of liver enzyme inducing antiepileptic drugs in people with active epilepsy: cohort study using the general practice research database. Seizure 2013;22:37ŌĆō42.


41. Verrotti A, Coppola G, Parisi P, Mohn A, Chiarelli F. Bone and calcium metabolism and antiepileptic drugs. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 2010;112:1ŌĆō10.


42. Vestergaard P, Rejnmark L, Mosekilde L. Fracture risk associated with use of antiepileptic drugs. Epilepsia 2004;45:1330ŌĆō7.


43. Riss J, Cloyd J, Gates J, Collins S. Benzodiazepines in epilepsy: pharmacology and pharmacokinetics. Acta Neurol Scand 2008;118:69ŌĆō86.


44. Ensrud KE, Walczak TS, Blackwell T, Ensrud ER, Bowman PJ, Stone KL. Antiepileptic drug use increases rates of bone loss in older women: a prospective study. Neurology 2004;62:2051ŌĆō7.


45. Kulak CA, Borba VZ, Bilezikian JP, Silvado CE, Paola L, Boguszewski CL. Bone mineral density and serum levels of 25 OH vitamin D in chronic users of antiepileptic drugs. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 2004;62:940ŌĆō8.



46. Hosseinpour F, Ellfolk M, Norlin M, Wikvall K. Phenobarbital suppresses vitamin D3 25-hydroxylase expression: a potential new mechanism for drug-induced osteomalacia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2007;357:603ŌĆō7.


47. Foss MC, Meneghelli UG, Tabosa Verissimo JM. The effect of the anticonvulsants phenobarbital and diphenylhydantoin on intestinal absorption of calcium. Acta Physiol Lat Am 1979;29:223ŌĆō8.

48. Koch HU, Kraft D, von Herrath D, Schaefer K. Influence of diphenylhydantoin and phenobarbital on intestinal calcium transport in the rat. Epilepsia 1972;13:829ŌĆō34.


49. Luoma PV, Reunanen MI, Sotaniemi EA. Changes in serum triglyceride and cholesterol levels during longterm phenytoin treatment for epilepsy. Acta Med Scand 1979;206:229ŌĆō31.


50. Harris M, Jenkins MV, Wills MR. Phenytoin inhibition of parathyroid hormone induced bone resorption in vitro. Br J Pharmacol 1974;50:405ŌĆō8.



51. Hahn TJ, Scharp CR, Richardson CA, Halstead LR, Kahn AJ, Teitelbaum SL. Interaction of diphenylhydantoin (phenytoin) and phenobarbital with hormonal mediation of fetal rat bone resorption in vitro. J Clin Invest 1978;62:406ŌĆō14.



52. Pack AM, Morrell MJ, Randall A, McMahon DJ, Shane E. Bone health in young women with epilepsy after one year of antiepileptic drug monotherapy. Neurology 2008;70:1586ŌĆō93.



53. Valimaki MJ, Tiihonen M, Laitinen K, Tahtela R, Karkkainen M, Lamberg-Allardt C, et al. Bone mineral density measured by dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry and novel markers of bone formation and resorption in patients on antiepileptic drugs. J Bone Miner Res 1994;9:631ŌĆō7.


54. Feldkamp J, Becker A, Witte OW, Scharff D, Scherbaum WA. Long-term anticonvulsant therapy leads to low bone mineral density--evidence for direct drug effects of phenytoin and carbamazepine on human osteoblast-like cells. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 2000;108:37ŌĆō43.



55. Takahashi A, Onodera K, Shinoda H, Mayanagi H. Phenytoin and its metabolite, 5-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-5-phenylhydantoin, show bone resorption in cultured neonatal mouse calvaria. Jpn J Pharmacol 2000;82:82ŌĆō4.


56. Ohta T, Wergedal JE, Gruber HE, Baylink DJ, Lau KH. Low dose phenytoin is an osteogenic agent in the rat. Calcif Tissue Int 1995;56:42ŌĆō8.



57. Vernillo AT, Rifkin BR, Hauschka PV. Phenytoin affects osteocalcin secretion from osteoblastic rat osteosarcoma 17/2.8 cells in culture. Bone 1990;11:309ŌĆō12.


58. von Borstel Smith M, Crofoot K, Rodriguez-Proteau R, Filtz TM. Effects of phenytoin and carbamazepine on calcium transport in Caco-2 cells. Toxicol In Vitro 2007;21:855ŌĆō62.


59. Sato Y, Kondo I, Ishida S, Motooka H, Takayama K, Tomita Y, et al. Decreased bone mass and increased bone turnover with valproate therapy in adults with epilepsy. Neurology 2001;57:445ŌĆō9.


60. Tekgul H, Serdaroglu G, Huseyinov A, Gokben S. Bone mineral status in pediatric outpatients on antiepileptic drug monotherapy. J Child Neurol 2006;21:411ŌĆō4.


61. Tsukahara H, Kimura K, Todoroki Y, Ohshima Y, Hiraoka M, Shigematsu Y, et al. Bone mineral status in ambulatory pediatric patients on long-term anti-epileptic drug therapy. Pediatr Int 2002;44:247ŌĆō53.


62. Babayigit A, Dirik E, Bober E, Cakmakci H. Adverse effects of antiepileptic drugs on bone mineral density. Pediatr Neurol 2006;35:177ŌĆō81.


63. Andress DL, Ozuna J, Tirschwell D, Grande L, Johnson M, Jacobson AF, et al. Antiepileptic drug-induced bone loss in young male patients who have seizures. Arch Neurol 2002;59:781ŌĆō6.


64. Pack AM, Morrell MJ, Marcus R, Holloway L, Flaster E, Done S, et al. Bone mass and turnover in women with epilepsy on antiepileptic drug monotherapy. Ann Neurol 2005;57:252ŌĆō7.



65. Kim SH, Lee JW, Choi KG, Chung HW, Lee HW. A 6-month longitudinal study of bone mineral density with antiepileptic drug monotherapy. Epilepsy Behav 2007;10:291ŌĆō5.


66. Nicolaidou P, Georgouli H, Kotsalis H, Matsinos Y, Papadopoulou A, Fretzayas A, et al. Effects of anticonvulsant therapy on vitamin D status in children: prospective monitoring study. J Child Neurol 2006;21:205ŌĆō9.


67. Boluk A, Guzelipek M, Savli H, Temel I, Ozisik HI, Kaygusuz A. The effect of valproate on bone mineral density in adult epileptic patients. Pharmacol Res 2004;50:93ŌĆō7.


68. Kumandas S, Koklu E, Gumus H, Koklu S, Kurtoglu S, Karakukcu M, et al. Effect of carbamezapine and valproic acid on bone mineral density, IGF-I and IGFBP-3. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 2006;19:529ŌĆō34.


69. Rieger-Wettengl G, Tutlewski B, Stabrey A, Rauch F, Herkenrath P, Schauseil-Zipf U, et al. Analysis of the musculoskeletal system in children and adolescents receiving anticonvulsant monotherapy with valproic acid or carbamazepine. Pediatrics 2001;108:E107.


70. Guo CY, Ronen GM, Atkinson SA. Long-term valproate and lamotrigine treatment may be a marker for reduced growth and bone mass in children with epilepsy. Epilepsia 2001;42:1141ŌĆō7.


71. Kafali G, Erselcan T, Tanzer F. Effect of antiepileptic drugs on bone mineral density in children between ages 6 and 12 years. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1999;38:93ŌĆō8.


72. Erbayat Altay E, Serdaroglu A, Tumer L, Gucuyener K, Hasanoglu A. Evaluation of bone mineral metabolism in children receiving carbamazepine and valproic acid. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 2000;13:933ŌĆō9.



73. Voudris K, Moustaki M, Zeis PM, Dimou S, Vagiakou E, Tsagris B, et al. Alkaline phosphatase and its isoenzyme activity for the evaluation of bone metabolism in children receiving anticonvulsant monotherapy. Seizure 2002;11:377ŌĆō80.


74. Oner N, Kaya M, Karasalihoglu S, Karaca H, Celtik C, Tutunculer F. Bone mineral metabolism changes in epileptic children receiving valproic acid. J Paediatr Child Health 2004;40:470ŌĆō3.


75. Akin R, Okutan V, Sarici U, Altunbas A, Gokcay E. Evaluation of bone mineral density in children receiving antiepileptic drugs. Pediatr Neurol 1998;19:129ŌĆō31.


76. Simm PJ, Bicknell-Royle J, Lawrie J, Nation J, Draffin K, Stewart KG, et al. The effect of the ketogenic diet on the developing skeleton. Epilepsy Res 2017;136:62ŌĆō6.


77. Schuh L, Barkley GL, Gates JR. Antiepileptic drugs and reduced bone mineral density. Epilepsy Behav 2004;5:296ŌĆō300.


78. Farhat G, Yamout B, Mikati MA, Demirjian S, Sawaya R, El-Hajj Fuleihan G. Effect of antiepileptic drugs on bone density in ambulatory patients. Neurology 2002;58:1348ŌĆō53.


79. Lazzari AA, Dussault PM, Thakore-James M, Gagnon D, Baker E, Davis SA, et al. Prevention of bone loss and vertebral fractures in patients with chronic epilepsy-antiepileptic drug and osteoporosis prevention trial. Epilepsia 2013;54:1997ŌĆō2004.


81. Valmadrid C, Voorhees C, Litt B, Schneyer CR. Practice patterns of neurologists regarding bone and mineral effects of antiepileptic drug therapy. Arch Neurol 2001;58:1369ŌĆō74.


82. Fewtrell MS. Bone densitometry in children assessed by dual x ray absorptiometry: uses and pitfalls. Arch Dis Child 2003;88:795ŌĆō8.



83. Kossoff EH, Zupec-Kania BA, Auvin S, Ballaban-Gil KR, Christina Bergqvist AG, Blackford R, et al. Optimal clinical management of children receiving dietary therapies for epilepsy: updated recommendations of the International Ketogenic Diet Study Group. Epilepsia Open 2018;3:175ŌĆō92.



84. Leet AI, Mesfin A, Pichard C, Launay F, Brintzenhofeszoc K, Levey EB, et al. Fractures in children with cerebral palsy. J Pediatr Orthop 2006;26:624ŌĆō7.


85. Stallings VA, Cronk CE, Zemel BS, Charney EB. Body composition in children with spastic quadriplegic cerebral palsy. J Pediatr 1995;126:833ŌĆō9.


86. Fehlings D, Switzer L, Agarwal P, Wong C, Sochett E, Stevenson R, et al. Informing evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for children with cerebral palsy at risk of osteoporosis: a systematic review. Dev Med Child Neurol 2012;54:106ŌĆō16.


87. Ozel S, Switzer L, Macintosh A, Fehlings D. Informing evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for children with cerebral palsy at risk of osteoporosis: an update. Dev Med Child Neurol 2016;58:918ŌĆō23.


88. Larson CM, Henderson RC. Bone mineral density and fractures in boys with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. J Pediatr Orthop 2000;20:71ŌĆō4.


89. McDonald DG, Kinali M, Gallagher AC, Mercuri E, Muntoni F, Roper H, et al. Fracture prevalence in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Dev Med Child Neurol 2002;44:695ŌĆō8.


90. King WM, Ruttencutter R, Nagaraja HN, Matkovic V, Landoll J, Hoyle C, et al. Orthopedic outcomes of longterm daily corticosteroid treatment in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Neurology 2007;68:1607ŌĆō13.


91. Birnkrant DJ, Bushby K, Bann CM, Alman BA, Apkon SD, Blackwell A, et al. Diagnosis and management of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, part 2: respiratory, cardiac, bone health, and orthopaedic management. Lancet Neurol 2018;17:347ŌĆō61.



92. Bianchi ML, Mazzanti A, Galbiati E, Saraifoger S, Dubini A, Cornelio F, et al. Bone mineral density and bone metabolism in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Osteoporos Int 2003;14:761ŌĆō7.



93. Bushby K, Finkel R, Birnkrant DJ, Case LE, Clemens PR, Cripe L, et al. Diagnosis and management of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, part 1: diagnosis, and pharmacological and psychosocial management. Lancet Neurol 2010;9:77ŌĆō93.


94. Ma J, McMillan HJ, Karaguzel G, Goodin C, Wasson J, Matzinger MA, et al. The time to and determinants of first fractures in boys with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Osteoporos Int 2017;28:597ŌĆō608.



95. Ferraris JR, Pasqualini T, Alonso G, Legal S, Sorroche P, Galich AM, et al. Effects of deflazacort vs. methylprednisone: a randomized study in kidney transplant patients. Pediatr Nephrol 2007;22:734ŌĆō41.



96. Ferraris JR, Pasqualini T, Legal S, Sorroche P, Galich AM, Pennisi P, et al. Effect of deflazacort versus methylprednisone on growth, body composition, lipid profile, and bone mass after renal transplantation. The Deflazacort Study Group. Pediatr Nephrol 2000;14:682ŌĆō8.



- TOOLS
- Related articles in APEM
-
Ciliopathies in pediatric endocrinology2023 March;28(1)
History of insulin treatment of pediatric patients with diabetes in Korea2021 December;26(4)
Updates on bone health in children with gastrointestinal diseases2020 March;25(1)
Spontaneous Growth in Korean Patients with Turner Syndrome.1998 May;3(1)







