Introduction
The skeleton acquires its strength and structure through mineralization [1]. The mineralized skeleton also functions as a reservoir for calcium and phosphorus. Decreased availability of calcium or phosphate leads to impaired mineralization in the form of rickets in children and osteomalacia in adults [2]. Tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase (TNSALP) facilitates skeletal mineralization by degrading pyrophosphate, an inhibitor of skeletal mineralization, to produce inorganic orthophosphate [3]. Inactivation of mutations in the gene that encodes TNSALP causes hypophosphatasia (HPP), an inherited disease characterized by impaired skeletal mineralization [4].
This review article summarizes and discusses current understanding of the mechanisms of skeletal mineralization and mineral homeostasis, and the pathogenesis of related diseases.
Matrix vesicle-mediated skeletal mineralization
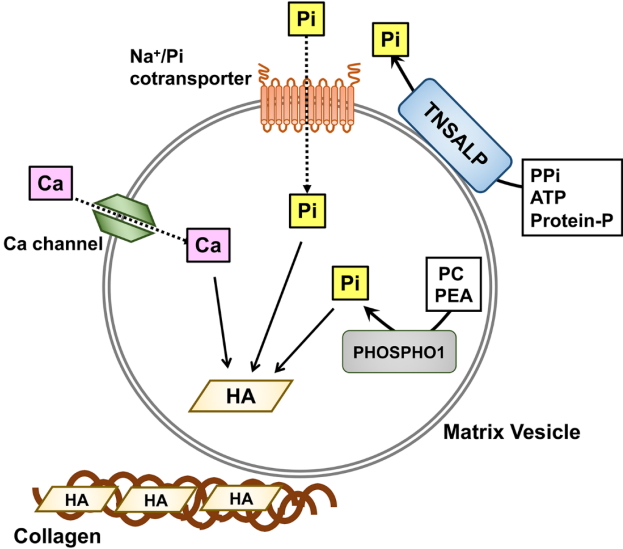
Skeletal mineralization is a well-regulated biological process. Although the precise mechanism is not fully understood yet, it has been suggested that matrix vesicles (MVs), the small extracellular vesicles derived from osteoblasts and chondrocytes, may initiate mineralization [5,6]. Inorganic phosphate (Pi) is transported into MVs via both sodium (Na+)-dependent and independent pathways, and the former are likely to be mediated by type III Na+/Pi co-transporters PiT-1 and PiT-2, in a manner similar to the uptake of Pi by the cells from which the MVs are derived [7]. Calcium and Pi ions taken up by MVs form hydroxyapatite crystals, which can propagate on collagen fibrils in the extracellular matrix (Fig. 1). TNSALP is an ectoenzyme on the outer surface of MVs that hydrolyzes its substrates, including pyrophosphate (PPi), adenosine triphosphate, and the protein-bound form of phosphate, to produce Pi [5,6]. Because PPi inhibits hydroxyapatite formation, TNSALP promotes skeletal mineralization by degrading PPi and producing Pi. Although recent mouse studies have shown that another phosphatase, PHOSPHO1, may be involved in the earliest step of mineralization by producing Pi within MVs from phosphocholine and phosphoethanolamine [8,9], its role in humans remains to be elucidated.
Calcium homeostasis and vitamin D
Extracellular calcium level is tightly regulated within a narrow range. Parathyroid hormone (PTH) accelerates osteoclastic bone resorption, which mobilizes calcium from the bone to extracellular fluid. An active metabolite of vitamin D, 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D (1,25(OH)2D), facilitates intestinal absorption of calcium [10,11]. In the intestine, calcium is absorbed by 2 kinds of transport processes: non-saturable paracellular absorption by passive diffusion, and active transcellular absorption. 1,25(OH)2D increases active transcellular absorption of calcium by upregulating expression of the calcium channel transient receptor potential vanilloid subfamily member 6 and the calcium binding protein calbindin-D9k [11]. This process is critical for sufficient absorption of calcium, especially when dietary calcium intake is low, and vitamin D deficiency is a significant cause of rickets/osteomalacia. When dietary calcium intake is high enough, passive paracellular transport compensates for deficient calcium absorption.
Vitamin D deficiency is common worldwide, even in developed countries. Global consensus recommendations were recently formulated, providing guidance for the prevention, diagnosis, and management of nutritional rickets caused by vitamin D and/or calcium deficiency [12]. Vitamin D deficiency is diagnosed based on low levels of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25OHD) [2,13]. When associated with insufficient calcium intake, vitamin D deficiency can lead to impaired skeletal mineralization. To prevent nutritional rickets and osteomalacia, it is therefore necessary to ensure that both the vitamin D status and calcium intake are sufficient [12].
Phosphate homeostasis
In addition to its central role in skeletal mineralization in vertebrates, phosphate is involved in almost all biological processes in all living organisms [14]. In adult humans, approximately 90% of the phosphorus in the body is stored in the skeleton as hydroxyapatite, with most of the remainder in the soft tissues [15]. The extracellular fluid contains less than 1% of the total phosphorus, mostly as Pi ions. Phosphate balance as a whole is maintained mainly by intestinal absorption, renal excretion, and accumulation to and release from the bones and soft tissues [14]. Insufficient intestinal Pi absorption, renal Pi wasting, or a shift of Pi into the cells can cause hypophosphatemia. Chronic hypophosphatemia leads to impaired skeletal mineralization.
Intestinal absorption of dietary phosphate is mediated by passive, paracellular diffusion, and active, transcellular transport [16]. Type IIb Na+/Pi co-transporter (NaPi-IIb), which is encoded by the SLC34A2 gene in humans and is localized in apical membrane of the small intestine epithelial cells, mediates active transcellular transport of Pi [17]. Intestinal expression of NaPi-IIb is up-regulated by low dietary phosphate intake and 1,25(OH)2D [18]. Dietary phosphate deficiency is less common than that of calcium, as almost all foods originate from cells containing high amounts of phosphate.
Excess Pi is excreted from the kidneys. The majority of the Pi filtered by the glomeruli is reabsorbed in proximal tubules by a transcellular, active transport. Type IIa and IIc Na+/Pi cotransporters (NaPi-IIa and NaPi-IIc), encoded by SLC34A1 and SLC34A3, respectively, are localized at the brush border membrane (BBM) of proximal tubules and mediate the reabsorption of Pi [19,20]. Inactivating mutations of SLC34A3 cause hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets with hypercalciuria, which is characterized by hypophosphatemia due to renal Pi wasting and secondary hypercalciuria caused by elevated levels of serum 1,25(OH)2D [21]. In addition, inactivating mutations of SLC34A1 have been identified in Fanconi renotubular syndrome 2, infantile hypercalciuria 2, and nephrolithiasis/osteoporosis associated with hypophosphatemia [14].
Endocrine factors such as PTH, 1,25(OH)2D, and fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) play critical roles in phosphate metabolism. PTH treatment causes a decrease in the protein amounts of NaPi-IIa [22] and NaPi-IIc [23] localized in the BBM, leading to increased renal excretion of phosphate. As described above, 1,25(OH)2D increases intestinal Pi absorption by upregulating NaPi-IIb.
FGF23, the central regulator of phosphate homeostasis, consists of 251 amino acids and a 24-amino acid signal peptide [24]. FGF23 belongs to the FGF19 subfamily, together with FGF19 and FGF21, based on their unique features, and act as endocrine factors that regulate diverse physiological processes. It has been suggested that their low binding affinity to heparin/heparan sulfate is responsible for the endocrine function of the FGF19 family members [25]. FGF23 is mainly produced by osteoblasts and osteocytes, and affects distant target organs [24]. FGF23 at physiological concentrations requires a single-pass transmembrane protein, ╬▒Klotho, for signal transduction through FGF receptors (FGFRs) [26,27], and organs and tissues expressing both FGFR and ╬▒Klotho, such as the kidneys, parathyroid glands [28], and placenta [29], can be targets for the physiological action of FGF23. The main target for FGF23 is the kidneys, where it suppresses NaPi-IIa and NaPi-IIc expression to increase urinary excretion of Pi. Moreover, FGF23 decreases the production of 1,25(OH)2D by suppressing renal expression of 25-hydroxyvitamin D 1╬▒-hydroxylase (1╬▒-hydroxylase) and induction of that of 25-hydroxyvitamin D-24-hydroxylase (24-hydroxylase), which leads to decreased intestinal absorption of Pi [24].
FGF23-associated diseases
Because FGF23 is the central regulator of phosphate homeostasis, excessive or impaired FGF23 signaling will lead to dysregulated phosphate metabolism. Impaired signaling of FGF23 can be caused by inactivating mutations in 3 genes, FGF23, GALNT3, and Klotho, and results in hyperphosphatemic familial tumoral calcinosis, which is characterized by hyperphosphatemia, normal or elevated levels of serum 1,25(OH)2D, and ectopic calcification. GALNT3 encodes UDP-N-acetyl-╬▒-D-galacosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgala ctosaminyltransferase 3 (GalNAc-T3), an enzyme mediating the O-glycosylation of FGF23, which prevents its proteolytic cleavage [24].
Excess activity of FGF23 underlies various hypophosphatemic conditions [30]. These diseases are characterized by increased urinary excretion, hypophosphatemia, inappropriately low levels of serum 1,25(OH)2D, and defects in skeletal mineralization. FGF23-related hypophosphatemia includes several hereditary diseases, among which autosomal dominant hypophosphatemic rickets (ADHR) is caused by missense mutations in the FGF23 gene itself at the amino acid Arg176 or Arg179 [31]. These arginines are located within the RXXR/S motif, the recognition site for cleavage by subtilisin-like proprotein convertase, and mutations in these residues make the FGF23 protein resistant to cleavage. However, levels of intact FGF23 are not always elevated in individuals with ADHR mutations, and clinical and translational studies have suggested the involvement of iron deficiency in the elevation of FGF23 levels and appearance of symptoms in ADHR [32,33].
FGF23-related hypophosphatemia also includes hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets caused by inactivating mutations in the phosphate-regulating gene with homologies to endopeptidases, on the X chromosome (PHEX), dentin matrix protein 1 (DMP1), ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase 1 (ENPP1), and family with sequence similarity 20 C (FAM20C) [2]. PHEX mutations are responsible for X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets (XLH), which is the most common form of hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets [34]. Although its structure suggests that PHEX functions as an endopeptidase, its physiological substrate remains to be determined.
Inactivating mutations in DMP1 and ENPP1 cause ADHR type I and type II, respectively [35-37]. DMP1 encodes an extracellular matrix protein belonging to the SIBLING (small integrin-binding ligand, N-linked glycoproteins) family. ENPP1 encodes an enzyme that produces PPi, which acts as an inhibitor of mineralization, as described earlier, and inactivating mutations in ENPP1 are also responsible for hypermineralization disorders such as generalized arterial calcification in infancy (GACI) [38].
FAM20C encodes a kinase that phosphorylates various secreted proteins [39]. The molecules phosphorylated by FAM20C include FGF23 and members of the SIBLING family such as DMP1 [40,41], osteopontin, and matrix extracellular phosphoglycoprotein. Inactivating mutations in FAM20C are responsible for Raine syndrome (RNS), an autosomal recessive disease characterized by neonatal osteosclerotic bone dysplasia and poor life prognosis. Surviving patients with a mild variant of RNS can manifest FGF23-related hypophosphatemia and dental abnormalities [42,43].
FGF23-related hypophosphatemic rickets/osteomalacia also includes tumor-induced osteomalacia, a paraneoplastic syndrome caused by overproduction of FGF23 from phosphaturic mesenchymal tumors; McCune-Albright syndrome caused by somatic activating mutations in GNAS1; linear nevus sebaceous syndrome caused by somatic mutations in KRAS/HRAS; and hypophosphatemia associated with intravenous administration of saccharated ferric oxide [2,44].
Among the molecules responsible for hereditary FGF23-related hypophosphatemic rickets, FGF23, PHEX, DMP1, and FAM20C are highly expressed in osteocytes, the dendritic cells that are differentiated from the osteoblasts and are embedded within the bone matrix [45]. Recent studies have revealed that osteocytes play central roles in bone homeostasis by sensing mechanical strain and controlling bone formation and resorption [46]. High levels of expression observed in phosphateregulating genes in osteocytes suggest that these cells also control the phosphate metabolism. Inactivating mutations in PHEX, DMP1, and FAM20C cause increased production of FGF23 in the osteocytes, suggesting that these molecules function as local negative regulators of FGF23.
Although the mechanism of FGF23 overproduction remains to be determined in most hereditary FGF23-related forms of hypophosphatemic rickets, mouse studies have suggested the involvement of enhanced FGFR signaling in the pathogenesis of XLH and ARHR1 [45,47,48]. We previously reported that osteocytic expression of classical FGF ligands (Fgf1 and Fgf2), their receptors (Fgfr1-3), and a target for FGFR signaling (early growth response 1) were up-regulated in Phex-deficient Hyp mice, a widely-used murine model for XLH, compared with those in wild-type mice [45]. In addition, Xiao et al. [48] has demonstrated that osteocyte-specific deletion of Fgfr1 in Hyp mice partially restored overproduction of FGF23. In addition, overproduction of FGF23 in Dmp1-knockout mice has been shown to be attributable to enhanced FGFR signaling in osteocytes [47]. In humans, osteoglophonic dysplasia caused by activating mutations in FGFR1 is often associated with increased FGF23 levels in serum and hypophosphatemia [49], supporting the notion that enhanced activation of FGFR signaling leads to increased production of FGF23 in the osteocytes.
In addition to its central roles in skeletal mineralization as a component of hydroxyapatite, recent studies, including our own, have demonstrated that extracellular Pi exerts regulates gene expression and cell behavior in skeletal cells [14]. It has been suggested that the signal evoked by increased extracellular Pi is transduced through FGFR and the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway [14,50-52]. This in turn suggests an intimate relationship between phosphate metabolism and FGFR. Given that FGFR is involved in transduction of signals triggered by extracellular Pi, enhanced FGFR signaling in Phex-deficient osteocytes may result in increased sensitivity to extracellular Pi. A Pi level may be sensed as "high" despite low environmental Pi, leading to the overproduction of FGF23 [14]. Fig. 2 shows a possible mechanism for FGF23 production in osteocytes of XLH.
Patients with XLH have been treated with active vitamin D and phosphorus [53], a treatment course that leads to a further increase in serum FGF23, which can worsen the disease. Recently, a neutralizing antibody against FGF23 (burosumab) has been developed as a new treatment for XLH, and beneficial effects have been reported [54].
Alkaline phosphatase and hypophosphatasia
As described earlier, TNSALP facilitates skeletal mineralization by degrading PPi and producing Pi. Inactivating mutations in the ALPL gene encoding TNSALP cause HPP, an inherited disease characterized by impaired skeletal mineralization and associated with low activity of TNSALP in the serum [4,55]. HPP has diverse clinical phenotypes and is usually classified into 6 subtypes: perinatal severe, perinatal benign, infantile, childhood, adult, and odonto HPP [56]. The perinatal severe form, which is also called perinatal lethal form, is the most severe type. Patients with this form manifest symptoms perinatally, including severe hypomineralization of the skeleton, respiratory failure and convulsions, and prognosis is poor unless treated with enzyme replacement. In contrast, the perinatal benign form is characterized by a good life prognosis despite perinatal onset of the disease. This form usually shows a bone deformity detectable in utero or soon after birth, but can improve spontaneously [57-59]. In infantile form, HPP patients may fail to thrive and show hypercalcemia/hypercalciuria, and approximately half of patients die early from respiratory failure. Patients with childhood form HPP can suffer from premature loss of deciduous teeth and rickets-like changes in the bones, while those with the adult form may have fragile bones. Patients with odonto HPP have only tooth involvement [4,55,56].
To date, more than 390 ALPL mutations have been identified in HPP. Perinatal or infantile HPP is nearly always autosomal recessive, while childhood, adult, and odonto HPP can be either autosomal recessive or autosomal dominant. In Japanese HPP, p.Leu520ArgfsX86 (c.1559delT) is the most frequent mutation and p.Phe327Leu (c.979T>C) is the second most frequent [60]. In vitro experiments in which wild-type and mutant TNSALP proteins were exogenously expressed in cultured cells have demonstrated that the p.Leu520ArgfsX86 mutant has almost no enzymatic activity, while the p.Phe327Leu mutant has substantial residual activity corresponding to ~70% of that of the wild-type protein [60]. Consistent with the in vitro enzymatic activity, patients with the homozygous mutation for p.Leu520ArgfsX86 manifest the perinatal severe phenotype while patients carrying p.Phe327Leu are classified to milder forms such as perinatal benign or odonto HPP.
Until recently, no effective treatment for the life-threatening perinatal severe and infantile forms of HPP was available. In 1982, Whyte et al. [61] reported a case in which a patient with life-threatening infantile HPP was given an infusion of plasma with high alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity derived from patients with Paget disease. Although the plasma ALP level transiently increased, there was no improvement in the skeletal mineralization. Thirty years later, an enzyme replacement therapy using a bone-targeting recombinant ALP (asfotase alfa) was developed, leading to a marked improvement in the life prognosis of life-threatening HPP [62]. Manufacture and sale of asfotase alfa were approved in Japan in July 2015, and in the EU, US, and Canada later the same year. In addition to its beneficial effects on skeletal mineralization and life prognosis in severe HPP, treatment with asfotase alfa may improve the motor function and quality of life of HPP patients [63].
Conclusion
Impaired skeletal mineralization is associated with various conditions, including vitamin D deficiency, renal Pi wasting, and inactivation of TNSALP. Because the treatments differ among these diseases, accurate diagnosis is important. Genetic testing is helpful for diagnosing inherited diseases such as hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets and HPP. Unraveling the pathogenesis has contributed to the development of new disease-specific drugs, such as burosumab for XLH and asfotase alfa for HPP.