 |
 |
- Search
| Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab > Volume 23(4); 2018 > Article |
|
Abstract
Thyroid dyshormonogenesis is characterized by impairment in one of the several stages of thyroid hormone synthesis and accounts for 10%–15% of congenital hypothyroidism (CH). Seven genes are known to be associated with thyroid dyshormonogenesis: SLC5A5 (NIS), SCL26A4 (PDS), TG, TPO, DUOX2, DUOXA2, and IYD (DHEAL1). Depending on the underlying mechanism, CH can be permanent or transient. Inheritance is usually autosomal recessive, but there are also cases of autosomal dominant inheritance. In this review, we describe the molecular basis, clinical presentation, and genetic diagnosis of CH due to thyroid dyshormonogenesis, with an emphasis on the benefits of targeted exome sequencing as an updated diagnostic approach.
Congenital hypothyroidism (CH) is the most common pediatric endocrinological disorder and an important cause of preventable mental retardation [1]. After the introduction of neonatal screening for CH, the incidence was 1 case per 3,684 live births [2], but the incidence has increased to 1 case per 1,000–2,000 live births of late [3]. Primary CH is usually caused by abnormal thyroid gland development, but 10%–15% of cases are caused by genetic defects in proteins involved in individual stages of thyroid hormone biosynthesis (thyroid dyshormonogenesis) [4]. The thyroid hormone biosynthesis pathway is well-characterized, including seven genes [5]. Thyroid dyshormonogenesis has been understood to be a biallelic disease, but there are reports of oligogenic and monoallelic cases [6]. Since phenotypes vary even among individuals with similar mutations, several factors determine disease severity [7]. CH can be categorized into permanent CH, which requires lifetime thyroid hormone replacement, and transient CH, characterized by a temporary thyroid hormone deficiency for the first few months or years after birth and later recovery of normal thyroid function [4].
Primary CH can be diagnosed biochemically by elevated serum thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and decreased thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) levels. For etiological diagnosis, thyroid ultrasonography, thyroid scintigraphy using 99mpertechnetate or 123I, or the perchlorate discharge test can be used [8].
In cases diagnosed as CH based on TSH, T4, and T3 values where an etiological diagnosis cannot be performed before starting levothyroxine (L-T4) replacement, it is recommended to stop L-T4 for a month at the age of 3 years and reevaluate the patient by biochemical tests and thyroid imaging [8]. However, the downside of thyroid scintigraphy and the perchlorate discharge test is that the patient is exposed to radiation. While thyroid scintigraphy is widely used to diagnose ectopic thyroid, the perchlorate discharge test is used relatively infrequently to differentiate the etiology of thyroid dyshormonogenesis. One reason is that the treatment for CH is always L-T4 replacement, irrespective of the cause. For the same reason, genetic diagnosis of thyroid dyshormonogenesis was not often conducted in the age of Sanger sequencing. Despite the lack of treatment implications, genetic diagnosis can provide insight into prognosis. Steady growth in the use of massively parallel sequencing (next-generation sequencing, NGS), including in Korea, where panel sequencing based on NGS (targeted exome sequencing) has been covered by insurance since 2017, we expect changes in the diagnostic approach to thyroid dyshormonogenesis.
Thus, we review the thyroid hormone biosynthesis pathway, followed by detailed summaries of genes in the pathway, including the frequencies and effects of mutations in these genes. Finally, we discuss the use of targeted exome sequencing for diagnosis.
The major substrates of thyroid hormone synthesis are iodine and tyrosine. The initial step in the thyroid hormone biosynthesis process is the binding of TSH to TSH receptors in the basolateral membrane of thyroid follicular cells, activating cyclic adenosine monophosphate [1]. Thyroid hormones are then synthesized in the thyroid gland in the following stages (Fig. 1).
Iodine (I) in food is absorbed in the form of iodide (I-) and travels to the thyroid gland in the boodstream. Iodide accumulates in thyroid follicular cells via sodium iodide symporter (NIS; SLC5A5) channels in the basolateral membrane of these cells [9]. NIS is an intrinsic transmembrane protein that actively transports iodide together with sodium. Ions such as perchlorate and pertechnetate are also transported to the thyroid gland by the same mechanisms and act as competitive inhibitors of iodide transport. Inside thyroid follicular cells, iodide rapidly diffuses to the apical membrane, where it is transported into colloid by pendrin (PDS; SLC26A4) channels [9].
Thyroglobulin is a glycoprotein synthesized within the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) of thyroid follicular cells; it forms exocytotic vesicles that migrate into the colloid via the apical membrane [10,11]. The tyrosine residues on thyroglobulin are used as substrates for the synthesis of thyroid hormone [11].
Iodide that has been transported to colloid undergoes oxidation to iodine, which is then covalently bound (organified) to the tyrosine residues in thyroglobulin to form monoiodotyrosine (MIT) and diiodotyrosine (DIT) [10]. The oxidation of iodide is catalyzed by thyroid peroxidase (TPO), and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is required for this reaction [12].
H2O2 required for the TPO-catalyzed reaction is produced by nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase complexes located on the apical membrane [13,14]. The oxidases producing H2O2 in the thyroid gland are dual oxidase 1 (DUOX1) and dual oxidase 2 (DUOX2); the latter is more important for maintaining normal thyroid function [1]. Dual oxidase maturation factor (DUOXA) translocates DUOX from the ER to the plasma membrane, and DUOXA2 dysfunction causes thyroid dyshormonogenesis [15].
In thyroglobulin molecules, T4 forms when two DITs combine and T3 forms when one MIT combines with one DIT. These reactions are also catalyzed by TPO [10].
To secrete T4 and T3, thyroglobulin is endocytosed by thyroid follicular cells in the form of colloid droplets. The droplets bind to lysosomes where they undergo hydrolysis, resulting in the release of T4, T3, DIT, and MIT. T4 and T3 are then secreted into the blood.
DIT and MIT released following the hydrolysis of thyroglobulin are converted into free iodide and tyrosine by iodotyrosine deiodinase (IYD) (also known as iodotyrosine dehalogenase 1 (DEHAL1)), and the free iodide and tyrosine are then utilized inside of follicular cells [16].
The genetic causes of thyroid dyshormonogenesis are summarized in Table 1 and in the following sections, which describe the roles of genes involved in the thyroid hormone biosynthesis pathway.
NIS is a 13-transmembrane domain glycoprotein that mediates active iodide transport in various tissues, such as the thyroid gland, salivary glands, stomach, lactating breasts, and small intestine [17]. NIS located on the basolateral membrane of the thyroid follicular cells actively transport one I- ion for every two Na+ ions, using the sodium gradient produced by Na+/K+ ATPase [17].
The first case of CH caused by an iodide transport defect was described by Stanbury and Chapman in 1960 [18]. Fujiwara et al. [19] first elucidated the molecular basis for an iodide transport defect, i.e., a mutation in the SLC5A5 gene. Since then, 15 mutations in SLC5A5 have been reported in the Human Gene Mutation Database (HGMD), and these show autosomal recessive inheritance [20]. Clinically, these mutations cause hypothyroidism accompanied by goiter with eutopic thyroid on thyroid ultrasonography but show low or absent radioactive iodine uptake (RAIU) in thyroid scintigraphy [21]. In addition, the stomach and salivary glands, which also contain NIS, are unable to uptake radioiodine [5]. Variation in the extent of hypothyroidism is related to a residual in vitro activity of mutant NIS [22]. In patients with residual NIS activity, thyroid function is improved by iodide supplementation; accordingly, iodide supplementation alone or in combination with L-T4 replacement is an appropriate treatment approach [1]. In Korea, there are no reported cases of CH caused by a mutation in SLC5A5 to date.
Pendrin is a multifunctional anion exchanger expressed in the thyroid, inner ear, and kidney; in the thyroid, pendrin is located in the apical membrane of follicular cells and is thought to mediate apical iodide transport [23]. Pendrin is encoded by the SLC26A4 gene. Homozygous or compound heterozygous mutations in SLC26A4 can cause Pendred syndrome [24], an autosomal recessive disease characterized by congenital bilateral sensorineural deafness and goiter and the most common cause of syndromic deafness [24]. To date, 539 SLC26A4 mutations have been reported in the HGMD [20]. However, not all mutations in SLC26A4 cause Pendred syndrome and approximately half of mutations cause deafness with normal thyroid function (nonsyndromic hearing loss with familial enlarged vestibular aqueduct or DFNB4) [1].
Hypothyroidism in Pendred syndrome is usually mild and often undetected in neonatal screening [25]. Goiter typically develops in childhood, but cases of congenital goiter have also been reported [26]. Iodide intake affects the thyroid phenotype, and congenital goiter is more common in iodine-deficient areas [5]. Although the perchlorate discharge test is usually positive, some patients show a normal test [27].
Thyroglobulin is the most abundantly expressed large homodimeric glycoprotein in the thyroid and acts as a matrix for the synthesis of thyroid hormone [11]. Thyroglobulin defects caused by mutations in TG are autosomal recessive and show a diverse clinical spectrum, ranging from a euthyroid state to severe hypothyroidism [11]. Most patients show congenital goiter or develop goiter soon after birth. There is a characteristic decrease in the serum thyroglobulin level [28]. Thyroglobulin defects caused by TG mutations lead to CH due to either quantitative or functional deficiency [29,30]. Functional deficiency can be caused by a thyroglobulin transport defect, where thyroglobulin accumulates in the ER and is not secreted into follicles, or by structural abnormalities in thyroglobulin leading to the reduced coupling and synthesis of MIT and DIT [30]. The first TG mutation was reported in 1991 [29], and 133 mutations have been reported in the HGMD to date [20].
TPO is a membrane-bound heme protein located in the apical membrane of thyroid follicular cells, and is involved in the coupling and tyrosyl iodination of thyroglobulin [10]. A biallelic mutation in TPO was first reported in 1992 [31], and currently 125 different mutations in TPO are reported in the HGMD [20]. Most patients show severe hypothyroidism and congenital goiter [5]. High RAIU is observed in scintigraphy, serum thyroglobulin level is elevated, and the perchlorate discharge test is positive [32]. CH caused by TPO mutations shows autosomal recessive inheritance, but approximately 20% of patients possess only a single TPO mutation [1]. This can be explained by unidentified mutations in intronic or regulatory regions, monoallelic expression of mutant TPO [33], or cosegregation of mutant and null TPO alleles [34].
DUOX2 produces H2O2, which is required for TPO-catalyzed reactions, while DUOXA2 acts as a maturation factor for DUOX2 [1,35].
CH caused by mutations in DUOX2 was first reported in 2002 and shows both autosomal recessive and autosomal dominant inheritance [36]. It was initially claimed that biallelic inactivating mutations cause severe and permanent CH, while monoallelic mutations are associated with mild and transient hypothyroidism [36]. However, later studies have reported biallelic mutations in DUOX2 in patients with transient hypothyroidism [37,38] and have shown that monoallelic mutations can cause permanent CH [7,39]. In a sequence analysis of DUOX2, TPO, TSHR, and TG in 43 patients with CH with eutopic thyroid gland in Korea, 23 patients (53.5%) had a sequence variant in DUOX2, indicating that DUOX2 mutations are a frequent genetic cause of thyroid dyshormonogenesis in Koreans [40]. Monoallelic and biallelic mutations can both cause transient or permanent CH, and there is no correlation between the phenotype and the number of mutant alleles [40]. Sequence analysis of DUOX2, DUOXA2, and TPO in 48 Japanese patients was performed, and DUOX2 mutations showed the highest frequency [41]. Currently, 159 different mutations in DUOX2 are reported in the HGMD [20].
CH caused by DUOX2 mutations is characterized by goiter, elevated TG, low free T4, and significantly elevated TSH, and most patients show PIOD in the perchlorate discharge test [7]. In patients with a DUOX2 defect, an excessive amount of dietary iodide facilitates better use of the H2O2 provided by DUOX1, indicating the potential for some compensation [42].
CH caused by DUOXA2 mutations was first detected in 2008 in patients who showed partial iodide organification defect (PIOD) but lacked mutations in TPO or DUOX2 [15]. The inheritance pattern is autosomal recessive, and 17 mutations have been reported in the HGMD [20]. However, in 2015, a monoallelic DUOXA2 mutation associated with transient CH was reported, emphasizing the need for further research [43].
IYD is a transmembrane protein located in the apical membrane of thyroid follicular cells, and releases free iodide from MIT and DIT, allowing it to be used again in thyroid hormone synthesis [44]. CH caused by IYD mutations was first reported in 2008 [45], and four mutations are currently reported in the HGMD [20]. Patients are characterized by normal thyroid function in neonatal screening, followed by the development of goiter and excessive urinary secretion of DIT and MIT in infancy and childhood [45]. Although inheritance is autosomal recessive, one heterozygous carrier developed goiter and hypothyroidism during follow-up monitoring [46].
Thyroid ultrasonography, thyroid scintigraphy or perchlorate discharge test can be used for etiological diagnosis [8]. In thyroid dyshormonogenesis, thyroid ultrasonography shows eutopic thyroid and depending on the severity of hypothyroidism, the thyroid size may be normal or large. Thyroid scintigraphy using 99mpertechnetate or 123I reflects NIS expression, because both 99mpertechnetate and 123I are captured by NIS [47]. When thyroid scintigraphy shows low or absent RAIU, this finding is suggestive of basolateral iodide transport defect (NIS mutations). Normal or high RAIU is suggestive of one of the dyshormonogenesis beyond iodide trapping [5,21]. In neonates and children, 99mpertechnetate is preferred for thyroid scintigraphy, since it results in less radiation exposure [47]. However, 99mpertechnetate is not organified. When thyroid scintigraphy shows normal or high RAIU, 123I scintigraphy with perchlorate discharge test can detect iodide organification defects [47]. In the perchlorate discharge test, first radioactive iodine is administered, sufficient time is allowed to pass so that the radioactive iodine is captured by the thyroid and then, perchlorate is administered orally. The perchlorate displaces nonorganified iodide from the thyroid. The perchlorate discharge test is considered positive (abnormal) if there is an abnormally rapid loss of radioactive iodine from the thyroid [48]. The release of ≥90% is defined as a total iodide organification defect (TIOD), while the release of 10%–90% is defined as a PIOD [49]. Homozygous or compound heterozygous TPO mutations lead to TIOD, whereas heterozygous TPO mutations show PIOD [49]. DUOX2 mutations also lead to TIOD or PIOD [5]. DUOXA2 mutations usually show PIOD [5]. Furthermore, PDS mutations show a positive perchlorate discharge test [49]. TG or IYD mutations usually show a negative perchlorate discharge test [5]. Although perchlorate discharge test is useful for diagnosing thyroid dyshormonogenesis, it may not suggest the specific underlying molecular mechanism.
Increased molecular diagnosis of primary CH has led to the discovery of various genetic causes and inheritance patterns for both thyroid dyshormonogenesis and thyroid dysgenesis. Most previous studies have focused on one or several genes that cause CH, and the study populations have usually been limited to subgroups of CH. Recently, in China, targeted exome sequencing has been used to evaluate 21 candidate genes known to cause CH (thyroid dysgenesis, thyroid dyshormonogenesis, and resistance to thyroid hormone) in 110 patients with primary CH [50]. Thyroid dyshormonogenesis is a more common cause of CH than thyroid dysgenesis in China, and mutations are most commonly observed in the DUOX2 gene [50].
From a practical perspective, thyroid dysgenesis can be easily diagnosed by thyroid imaging without knowing the genetic cause. The incidence of CH detected by neonatal screening has increased, with a particular increase in the incidence of CH with eutopic thyroid. A large proportion of these cases are expected to be thyroid dyshormonogenesis. Thyroid dyshormonogenesis can cause permanent or transient CH depending on the genetic cause, and often goes undiagnosed in neonatal screening and does not show symptoms until later. The genetic diagnosis of thyroid dyshormonogenesis using targeted exome sequencing could provide great benefits not only to current patients but also in genetic counselling for subsequent generations.
Thyroid dyshormonogenesis could be a more common cause of CH than was previously understood. Thyroid dyshormonogenesis can cause permanent or transient CH, depending on the genetic cause, and shows both autosomal recessive and autosomal dominant inheritance patterns. Targeted exome sequencing of 7 causative genes for thyroid dyshormonogenesis could improve the prediction of prognoses for current patients and could be useful for genetic counselling for subsequent generations.
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of thyroid hormone biosysynthesis. DIT, diiodotyrosine; DUOX2, dual oxidase 2; DUOXA2, dual oxidase maturation factor 2; TPO, thyroid peroxidase; IYD, iodotyrosine deiodinase; MIT, monoiodotyrosine; NIS, sodium iodide symporter; TG, thyroglobulin; TSHR, thyroid stimulating hormone receptor.
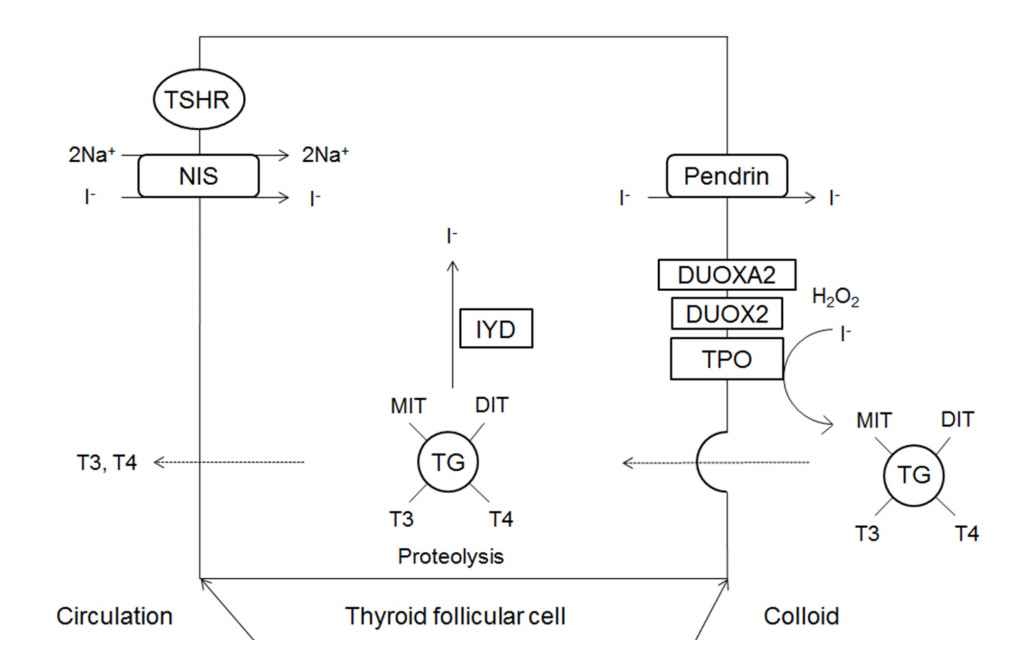
Table 1.
Causes of thyroid dyshormonogenesis
References
1. Grasberger H, Refetoff S. Genetic causes of congenital hypothyroidism due to dyshormonogenesis. Curr Opin Pediatr 2011;23:421–8.



2. Fisher DA, Dussault JH, Foley TP Jr, Klein AH, LaFranchi S, Larsen PR, et al. Screening for congenital hypothyroidism: results of screening one million North American infants. J Pediatr 1979;94:700–5.


3. LaFranchi SH. Increasing incidence of congenital hypothyroidism: some answers, more questions. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2011;96:2395–7.


6. Nicholas AK, Serra EG, Cangul H, Alyaarubi S, Ullah I, Schoenmakers E, et al. Comprehensive screening of eight known causative genes in congenital hypothyroidism with gland-in-situ. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2016;101:4521–31.



7. Muzza M, Rabbiosi S, Vigone MC, Zamproni I, Cirello V, Maffini MA, et al. The clinical and molecular characterization of patients with dyshormonogenic congenital hypothyroidism reveals specific diagnostic clues for DUOX2 defects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2014;99:E544–53.



8. Léger J, Olivieri A, Donaldson M, Torresani T, Krude H, van Vliet G, et al. European Society for Paediatric Endocrinology consensus guidelines on screening, diagnosis, and management of congenital hypothyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2014;99:363–84.




10. Knobel M, Medeiros-Neto G. An outline of inherited disorders of the thyroid hormone generating system. Thyroid 2003;13:771–801.


11. Targovnik HM, Esperante SA, Rivolta CM. Genetics and phenomics of hypothyroidism and goiter due to thyroglobulin mutations. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2010;322:44–55.


12. Muzza M, Fugazzola L. Disorders of H(2)O(2) generation. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 2017;31:225–40.


13. De Deken X, Wang D, Many MC, Costagliola S, Libert F, Vassart G, et al. Cloning of two human thyroid cDNAs encoding new members of the NADPH oxidase family. J Biol Chem 2000;275:23227–33.


14. Grasberger H, Refetoff S. Identification of the maturation factor for dual oxidase. Evolution of an eukaryotic operon equivalent. J Biol Chem 2006;281:18269–72.


15. Zamproni I, Grasberger H, Cortinovis F, Vigone MC, Chiumello G, Mora S, et al. Biallelic inactivation of the dual oxidase maturation factor 2 (DUOXA2) gene as a novel cause of congenital hypothyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2008;93:605–10.



16. Moreno JC. Identification of novel genes involved in congenital hypothyroidism using serial analysis of gene expression. Horm Res 2003;60 Suppl 3:96–102.


17. Portulano C, Paroder-Belenitsky M, Carrasco N. The Na+/I- symporter (NIS): mechanism and medical impact. Endocr Rev 2014;35:106–49.



18. Stanbury JB, Chapman EM. Congenital hypothyroidism with goitre. Absence of an iodide-concentrating mechanism. Lancet 1960;1:1162–5.


19. Fujiwara H, Tatsumi K, Miki K, Harada T, Miyai K, Takai S, et al. Congenital hypothyroidism caused by a mutation in the Na+/I- symporter. Nat Genet 1997;16:124–5.



20. The Human Gene Mutation Database [Internet]. Cardiff (UK), Cardiff University. 2015;[cited 2018 Jul 23]. Available from: http://www.hgmd.cf.ac.uk.
21. Hannoush ZC, Weiss RE. Defects of thyroid hormone synthesis and action. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 2017;46:375–88.



22. Szinnai G, Kosugi S, Derrien C, Lucidarme N, David V, Czernichow P, et al. Extending the clinical heterogeneity of iodide transport defect (ITD): a novel mutation R124H of the sodium/iodide symporter gene and review of genotypephenotype correlations in ITD. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2006;91:1199–204.


23. Everett LA, Green ED. A family of mammalian anion transporters and their involvement in human genetic diseases. Hum Mol Genet 1999;8:1883–91.



24. Everett LA, Glaser B, Beck JC, Idol JR, Buchs A, Heyman M, et al. Pendred syndrome is caused by mutations in a putative sulphate transporter gene (PDS). Nat Genet 1997;17:411–22.



25. Banghova K, Al Taji E, Cinek O, Novotna D, Pourova R, Zapletalova J, et al. Pendred syndrome among patients with congenital hypothyroidism detected by neonatal screening: identification of two novel PDS/SLC26A4 mutations. Eur J Pediatr 2008;167:777–83.


27. Ladsous M, Vlaeminck-Guillem V, Dumur V, Vincent C, Dubrulle F, Dhaenens CM, et al. Analysis of the thyroid phenotype in 42 patients with Pendred syndrome and nonsyndromic enlargement of the vestibular aqueduct. Thyroid 2014;24:639–48.


28. Targovnik HM, Citterio CE, Rivolta CM. Iodide handling disorders (NIS, TPO, TG, IYD). Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 2017;31:195–212.


29. Ieiri T, Cochaux P, Targovnik HM, Suzuki M, Shimoda S, Perret J, et al. A 3' splice site mutation in the thyroglobulin gene responsible for congenital goiter with hypothyroidism. J Clin Invest 1991;88:1901–5.



30. Medeiros-Neto G, Kim PS, Yoo SE, Vono J, Targovnik HM, Camargo R, et al. Congenital hypothyroid goiter with deficient thyroglobulin. Identification of an endoplasmic reticulum storage disease with induction of molecular chaperones. J Clin Invest 1996;98:2838–44.



31. Abramowicz MJ, Targovnik HM, Varela V, Cochaux P, Krawiec L, Pisarev MA, et al. Identification of a mutation in the coding sequence of the human thyroid peroxidase gene causing congenital goiter. J Clin Invest 1992;90:1200–4.



32. Ris-Stalpers C, Bikker H. Genetics and phenomics of hypothyroidism and goiter due to TPO mutations. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2010;322:38–43.


33. Fugazzola L, Cerutti N, Mannavola D, Vannucchi G, Fallini C, Persani L, et al. Monoallelic expression of mutant thyroid peroxidase allele causing total iodide organification defect. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003;88:3264–71.


34. Kotani T, Umeki K, Yamamoto I, Ohtaki S, Adachi M, Tachibana K. Iodide organification defects resulting from cosegregation of mutated and null thyroid peroxidase alleles. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2001;182:61–8.


35. Morand S, Ueyama T, Tsujibe S, Saito N, Korzeniowska A, Leto TL. Duox maturation factors form cell surface complexes with Duox affecting the specificity of reactive oxygen species generation. FASEB J 2009;23:1205–18.



36. Moreno JC, Bikker H, Kempers MJ, van Trotsenburg AS, Baas F, de Vijlder JJ, et al. Inactivating mutations in the gene for thyroid oxidase 2 (THOX2) and congenital hypothyroidism. N Engl J Med 2002;347:95–102.


37. Maruo Y, Takahashi H, Soeda I, Nishikura N, Matsui K, Ota Y, et al. Transient congenital hypothyroidism caused by biallelic mutations of the dual oxidase 2 gene in Japanese patients detected by a neonatal screening program. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2008;93:4261–7.



38. Enacán RE, Masnata ME, Belforte F, Papendieck P, Olcese MC, Siffo S, et al. Transient congenital hypothyroidism due to biallelic defects of DUOX2 gene. Two clinical cases. Arch Argent Pediatr 2017;115:e162–5.

39. Wang F, Lu K, Yang Z, Zhang S, Lu W, Zhang L, et al. Genotypes and phenotypes of congenital goitre and hypothyroidism caused by mutations in dual oxidase 2 genes. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2014;81:452–7.


40. Jin HY, Heo SH, Kim YM, Kim GH, Choi JH, Lee BH, et al. High frequency of DUOX2 mutations in transient or permanent congenital hypothyroidism with eutopic thyroid glands. Horm Res Paediatr 2014;82:252–60.


41. Matsuo K, Tanahashi Y, Mukai T, Suzuki S, Tajima T, Azuma H, et al. High prevalence of DUOX2 mutations in Japanese patients with permanent congenital hypothyroidism or transient hypothyroidism. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 2016;29:807–12.



42. Vigone MC, Fugazzola L, Zamproni I, Passoni A, Di Candia S, Chiumello G, et al. Persistent mild hypothyroidism associated with novel sequence variants of the DUOX2 gene in two siblings. Hum Mutat 2005;26:395.

43. Liu S, Liu L, Niu X, Lu D, Xia H, Yan S. A novel missense mutation (I26M) in DUOXA2 causing congenital goiter hypothyroidism impairs NADPH oxidase activity but not protein expression. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2015;100:1225–9.


44. Gnidehou S, Caillou B, Talbot M, Ohayon R, Kaniewski J, Noël-Hudson MS, et al. Iodotyrosine dehalogenase 1 (DEHAL1) is a transmembrane protein involved in the recycling of iodide close to the thyroglobulin iodination site. FASEB J 2004;18:1574–6.


45. Moreno JC, Klootwijk W, van Toor H, Pinto G, D'Alessandro M, Lèger A, et al. Mutations in the iodotyrosine deiodinase gene and hypothyroidism. N Engl J Med 2008;358:1811–8.


46. Afink G, Kulik W, Overmars H, de Randamie J, Veenboer T, van Cruchten A, et al. Molecular characterization of iodotyrosine dehalogenase deficiency in patients with hypothyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2008;93:4894–901.



47. Keller-Petrot I, Leger J, Sergent-Alaoui A, de Labriolle-Vaylet C. Congenital hypothyroidism: role of nuclear medicine. Semin Nucl Med 2017;47:135–42.


48. Leslie WD. Thyroid scintigraphy and perchlorate discharge test in the diagnosis of congenital hypothyroidism. Eur J Nucl Med 1996;23:230.









