|
 |
- Search
| Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab > Volume 21(1); 2016 > Article |
|
Abstract
Adrenocorticotropin-independent adrenal hyperplasias are rare diseases, which are classified into macronodular (>1 cm) and micronodular (Ōēż1 cm) hyperplasia. Micronodular adrenal hyperplasia is subdivided into primary pigmented adrenocortical disease and a limited or nonpigmented form 'micronodular adrenocortical disease (MAD)', although considerable morphological and genetic overlap is observed between the 2 groups. We present an unusual case of a 44-month-old girl who was diagnosed with Cushing syndrome due to MAD. She had presented with spotty pigmentation on her oral mucosa, lips and conjunctivae and was diagnosed with multiple bone tumors in her femur, pelvis and skull base at the age of 8 years. Her bone tumor biopsies were compatible with osteoblastoma. This case highlights the importance of verifying the clinicopathologic correlation in Cushing syndrome and careful follow-up and screening for associated diseases.
Cushing syndrome (CS) is a disease resulting from glucocorticoid excess1). The incidence of endogenous CS is reportedly 2ŌĆō3 per million cases per year, and approximately 10% of cases are diagnosed during childhood 2,3). Endogenous CS is classified as adrenocorticotropin (ACTH)-dependent and ACTH-independent CS. ACTH-dependent Cushing disease, which comprises 70% of endogenous CS, is more common in adults and children of older age. ACTH-independent CS is more common in young children4) and is attributed to primary cortisol-producing adrenocortical lesions, which are adrenocortical tumors, adrenocortical carcinomas and primary adrenocortical hyperplasias. ACTH-independent CS is also associated with various diseases and genetic defects5,6).
We introduce an unusual case of a child with CS due to primary bilateral adrenal micronodular hyperplasia with spotty pigmentations on her conjunctivae and oral mucosa who had multiple osteoblastomas.
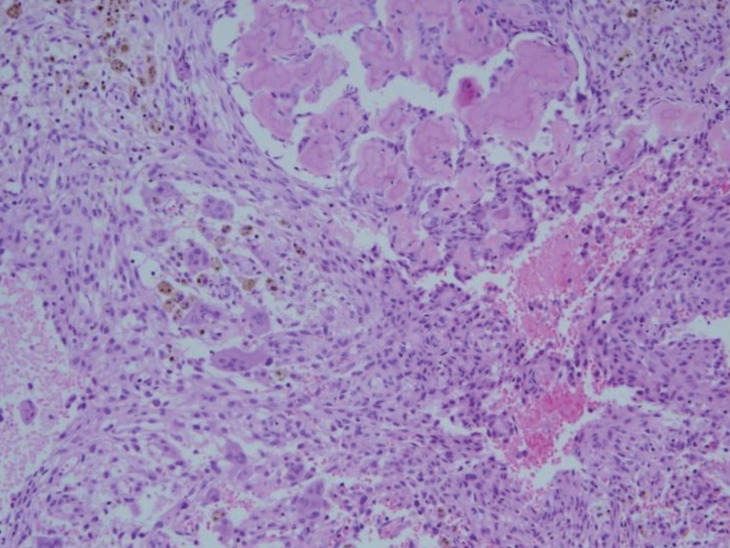
A 44-month-old girl was admitted who complained of excessive weight gain with growth failure and mood change. Her blood pressure was 150/80 mmHg, height was 96 cm (25th percentile), weighed 19.7 kg (>97th percentile) and her body mass index was 21.4 kg/m2 (>97th percentile). Plethoric moon face, hypertrichosis, and spotty pigmentation on her conjunctivae, lip and oral mucosa were observed. There was no specific medical history, including tumor or adrenal disease, in her family. Her urinary cortisol level was 966.2 ┬Ąg/m2/24 hr (reference range [RR], <70 ┬Ąg/m2/24 hr7)), and her serum cortisol level after a high dose dexamethasone suppression test was basal 34.6 ┬Ąg/dL (RR, 5ŌĆō23 ┬Ąg/dL), peak 32.9 ┬Ąg/dL (RR, <5 ┬Ąg/dL). The 24-hour urine cortisol levels of six-day Liddle's dexamethasone suppression test revealed following values; 1,380.0; 1,357.2; 1,064.4; 897.0; 944.0; 755.6 ┬Ąg/24 hr from day 1 to 6, respectively. The result was compatible to adrenal CS and no paradoxical increase was observed. Whereas her symptoms and signs of cortisol excess were very prominent, and her blood and urine cortisol levels were increased significantly, her computed tomography of the adrenal gland revealed 5-mm nodular thickening of the left adrenal gland and a nearly normal right adrenal gland (Fig. 1). She underwent laparoscopic left adrenalectomy at the age of 47 months. Because her symptoms of excess cortisol and increased urinary cortisol levels remained after left adrenalectomy, right adrenalectomy was performed at 58 months. The pathology of both adrenal glands revealed adrenocortical micronodular hyperplasia without apparent pigmentation, which was more compatible with micronodular adrenocortical disease (MAD) than primary pigmented adrenocortical disease (PPNAD) (Fig. 2).
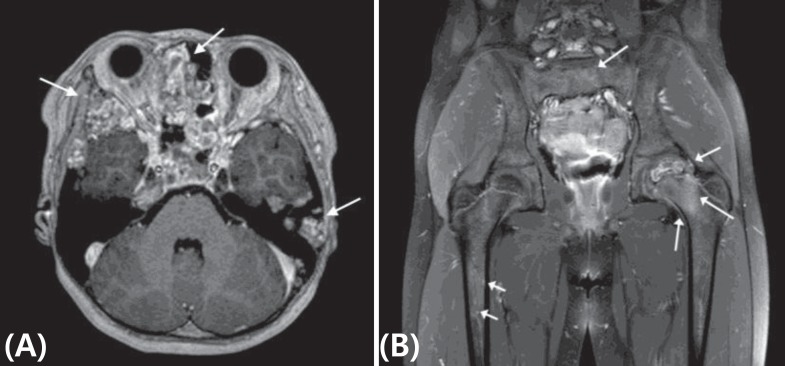
Because her skin pigmentation and pathology of both adrenal glands suggested the possibility of Carney complex, heart and thyroid gland ultrasonography were performed, which were all negative. No deletion or duplication was identified in protein kinase A regulatory subunit type 1A (PRKAR1A) gene analysis. However, at the age of 8 years, she complained of left hip pain, and her physical exam suspected a bone protrusion in the left temporal area. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of her hip revealed overall polyostotic bone tumors involving the bilateral femurs, ilium and sacrum. Her brain MRI revealed multiple multilocular cystic bone lesions involving the clivus, bifrontal skull base, bilateral sphenoid, and left temporal bones (Fig. 3). The right temporal bone biopsy demonstrated osteoid producing neoplasms, consistent with osteoblastoma (Fig. 4). Because the bone pain had resolved and the skull, hip and leg lesions caused no functional problems, she was on conservative management with physiologic hydrocortisone and fludrocortisone replacement.
Primary bilateral adrenal hyperplasias are rare diseases, the incidence of which is estimated to be up to 10% of ACTH-independent CS5). Bilateral adrenal hyperplasias are classified into 2 groups by the diameter of the associated nodules (macronodular, >1 cm; micronodular, Ōēż1 cm)5,6). While primary bilateral macronodular adrenocortical hyperplasia has a slight male predominance, micronodular hyperplasia has a slight female predominance and tends to arise at a younger age5,6). In cases of primary adrenal hyperplasia, medical treatments such as ketoconazole or mitotane which inhibits the biosynthesis of steroid can be used but has little effect. Eventually, unilateral (in case of adrenal adenoma or carcinoma) or bilateral adrenalectomy (in case of bilateral adrenal hyperplasia) is necessary4).
Micronodular adrenal hyperplasia is subdivided into a pigmented form 'PPNAD' and a limited or nonpigmented form 'MAD', although considerable morphological and genetic overlap is observed between the two groups6,8). In most of individuals with MAD, the adrenal glands had an overall normal size and multiple small yellow-to-dark brown nodules that were surrounded by a cortex with a uniform appearance. Microscopically, there was moderate diffuse cortical hyperplasia with mostly nonpigmented nodules9).
While MAD is usually an isolated disease, and the associated disease has not defined with MAD5,6), PPNAD typically occurs in the setting of Carney complex, which presents as cardiac myxoma and benign tumors in other body parts. The pathogenesis of Carney complex has been attributed predominantly to an inactivating germline mutation in protein kinase A regulatory-subunit type 1╬▒ (PRKAR1A) and in rare circumstance to alterations of the Carney complex type 2 (CNC2) gene loci. MAD cases have been associated with inactivating mutations in phosphodiesterase genes (PDE11A, PDE8B), and alterations of 2p12-p16 and 5q5,6,8,9).
Our patient demonstrated spotty skin, mucosal pigmentation and micronodular adrenal hyperplasia, which suggested Carney complex. However, a paradoxical increase in the 6-day Liddle's dexamethasone suppression test, which has been described in patients with PPNAD, did not present, and PRKAR1A mutations were negative in this case. Moreover, the pathology revealed neither pigmentation nor internodular atrophy of the adrenal cortex, which was more favorable to MAD. Bone tumors associated with Carney complex are known as osteochondromyxomas. They usually present without pain and are detected during the imaging evaluation of mass side effects, and pathology reveals osteolytic lesions composed of myxoid matrix10,11). However, in our case, the first presenting bone tumor symptoms were pain and bone protrusion, and biopsy revealed osteoid producing neoplasm, consistent with osteoblastoma. This suggests that the bone tumor is a different entity in this case rather than related bone tumors such as Carney complex. Since osteoblastomas are a benign bone forming tumor, surgical curettage or resection are needed if symptoms are present or bone destructions are observed12). About 26.6% of the patients are treated nonsurgically. And among the patients who underwent surgical procedure, recurrence rate after the surgery is 24.4%12,13). But in our case, the pain was resolved and no other functional problem occurred, so conservative therapy was done without any surgery.
While MAD is usually an isolated case, our case is the first reported case that presented with spotty pigmentation and multiple osteoblastomas. Judging by the above-mentioned information, we can cautiously conclude that this patient might have a proliferation malfunction or a mutation in a tumor suppressor gene. Although we could not find the exact gene, we should carefully screen due to probabilities of other neoplasms.
Various symptoms and clinical outcomes can result from CS, which makes the diagnosis difficult and subtle. This case highlights the importance of verifying the etiology of CS as well as careful follow-up and screening for associated diseases.
References
1. Magiakou MA, Mastorakos G, Oldfield EH, Gomez MT, Doppman JL, Cutler GB Jr, et al. Cushings syndrome in children and adolescents. Presentation, diagnosis, and therapy. N Engl J Med 1994;331:629ŌĆō623. PMID: 8052272.


2. Nieman LK, Biller BM, Findling JW, Newell-Price J, Savage MO, Stewart PM, et al. The diagnosis of Cushing's syndrome: an Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2008;93:1526ŌĆō1540. PMID: 18334580.




3. Sharma ST, Nieman LK, Feelders RA. Cushing's syndrome: epidemiology and developments in disease management. Clin Epidemiol 2015;7:281ŌĆō293. PMID: 25945066.


4. Boscaro M, Barzon L, Fallo F, Sonino N. Cushing's syndrome. Lancet 2001;357:783ŌĆō791. PMID: 11253984.


5. Stratakis CA, Boikos SA. Genetics of adrenal tumors associated with Cushing's syndrome: a new classification for bilateral adrenocortical hyperplasias. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab 2007;3:748ŌĆō757. PMID: 17955016.


6. Duan K, Gomez Hernandez K, Mete O. Clinicopathological correlates of adrenal Cushing's syndrome. J Clin Pathol 2015;68:175ŌĆō186. PMID: 25425660.


7. Batista DL, Riar J, Keil M, Stratakis CA. Diagnostic tests for children who are referred for the investigation of Cushing syndrome. Pediatrics 2007;120:e575ŌĆōe586. PMID: 17698579.


8. Carney JA, Gaillard RC, Bertherat J, Stratakis CA. Familial micronodular adrenocortical disease, Cushing syndrome, and mutations of the gene encoding phosphodiesterase 11A4 (PDE11A). Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:547ŌĆō555. PMID: 20351491.



9. Almeida MQ, Stratakis CA. Carney complex and other conditions associated with micronodular adrenal hyperplasias. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 2010;24:907ŌĆō914. PMID: 21115159.



10. Carney JA, Boccon-Gibod L, Jarka DE, Tanaka Y, Swee RG, Unni KK, et al. Osteochondromyxoma of bone: a congenital tumor associated with lentigines and other unusual disorders. Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:164ŌĆō176. PMID: 11176065.


11. Courcoutsakis NA, Tatsi C, Patronas NJ, Lee CC, Prassopoulos PK, Stratakis CA. The complex of myxomas, spotty skin pigmentation and endocrine overactivity (Carney complex): imaging findings with clinical and pathological correlation. Insights Imaging 2013;4:119ŌĆō133. PMID: 23315333.




12. Berry M, Mankin H, Gebhardt M, Rosenberg A, Hornicek F. Osteoblastoma: a 30-year study of 99 cases. J Surg Oncol 2008;98:179ŌĆō183. PMID: 18561158.


13. Burn SC, Ansorge O, Zeller R, Drake JM. Management of osteoblastoma and osteoid osteoma of the spine in childhood. J Neurosurg Pediatr 2009;4:434ŌĆō438. PMID: 19877775.


Fig.┬Ā1
Computed tomography of the adrenal gland. Horizontal view of the abdomen revealed 5-mm nodular thickening of the left adrenal gland and a nearly normal right adrenal gland (black arrow).

Fig.┬Ā2
Pathology of both adrenal glands. (A) The right adrenal gland measured 4 cm├Ś3 cm├Ś0.7 cm, and the left adrenal gland measured 5.5 cm├Ś3.2 cm├Ś1.5 cm. The adrenal glands are enlarged and have multiple micronodules on the cut surface (white arrows). Microscopically, circumscribed small nodules are observed in the adrenal cortex, and the nodule diameter usually does not exceed 0.5 cm. No pigment granules are observed. H&E staining (B: ├Ś40; C: ├Ś100).
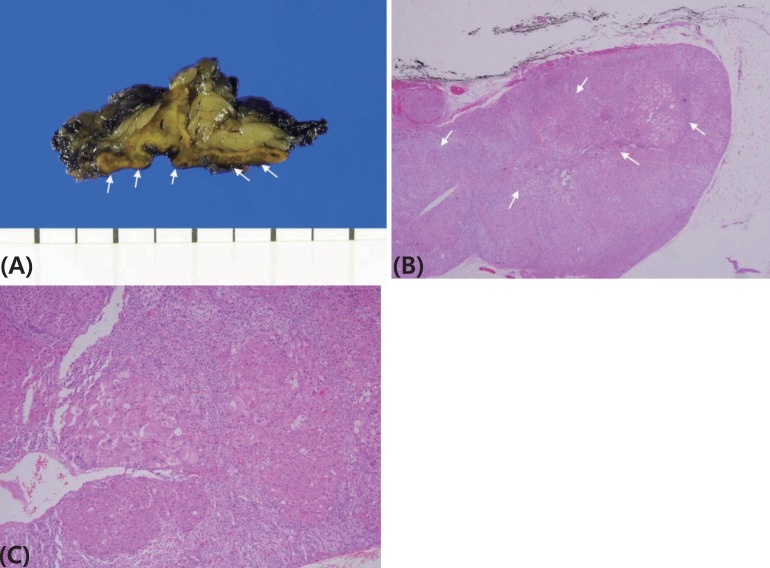
Fig.┬Ā3
Magnetic resonance imaging of brain and hip. (A) Horizontal view of the brain demonstrates multiple multilocular cystic bone lesions with internal hemorrhage and prominent wall enhancements involving the clivus, bifrontal skull base, bilateral sphenoid and left temporal bones (white arrows). (B) Coronal view of the hip with section at the femur head level revealed overall polyostotic bone tumors involving bilateral femurs as well as the ilium and sacrum (white arrows)
- TOOLS
-
METRICS

-
- 2 Crossref
- Scopus
- 8,506 View
- 146 Download
- Related articles in APEM
-
Adrenocortical Carcinoma in a Patient with Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia.2010 December;15(3)